The birth of guinea pigs is the most important process in the breeding of these animals. For everything to go well, the owner must know what to do in case of complications, what kind of help the pet needs during delivery, and how to handle the babies. The animal is capable of producing healthy offspring starting from seven months of age. Guinea pigs give birth twice a year - this figure should not be increased. Gestation lasts 60–72 days, and one litter can contain from one to seven cubs. Newborn babies are fully formed mini-pigs - they have all their teeth, their eyes are open, and a few hours after birth they are already starting to crawl.
Puberty
Appears quite early:
- The first heat in females is observed at 8 weeks,
- males mature a little later - usually by three months of age.
But puberty does not mean that rodents can and should mate. At such a young age, the body is not fully formed, and mating will not give the expected results: either fertilization will not occur, or the litter will not be viable.
In addition, early coating seriously undermines the health of the pet, especially females. After unjustified haste throughout her life, she will often get sick, and, consequently, bear weak and underdeveloped offspring. The danger of early mating also lies in the possible death of the animal during childbirth, when the pelvis and birth canal are not yet sufficiently developed.
Experienced breeders recommend using animals at least 10 months old to produce healthy offspring. In some cases, younger six-month-old individuals are also used for these purposes.
It is important to understand that living conditions, diet, and breed play a significant role in the onset of puberty.
What to feed a baby guinea pig
For the first three weeks, the cubs feed on their mother's milk. Additionally, they are offered adult food so that they get used to it in advance. Babies are able to eat regular food from 2 to 3 days. They are offered their mother's standard diet:
- compound feed;
- herbal granules;
- nuts;
- hay:
- vegetables: carrots, cucumber:
- fruits in limited quantities.
You should check the freshness of the food and remove any old portions from the cage. The immunity of cubs is weaker than that of adults, so food poisoning is difficult for them.
It is natural for all pigs to eat a small amount of their own (or, in the case of cubs, their mother's) droppings, which contain vitamins K and B that have not had time to be absorbed during initial digestion.
Hay is an important component of a pig's diet. It promotes stable intestinal function and helps animals wear down their teeth, which grow continuously throughout life. It is important to ensure that the hay is dry and aromatic. Spoiled - wet or rotten - will lead to the death of animals.
In most cases, a nursing pig takes care of its offspring independently. The owner is required to provide the animals with sufficient food and water and create a quiet, calm atmosphere in the room. Following simple rules for keeping mother and cubs will help the latter grow into healthy pets that are friendly towards people.
Selection of animals for breeding
It matters a lot. Pigs must be:
- well-fed,
- agile and cheerful,
- absolutely healthy,
- have excellent breed qualities,
- with wool of excellent quality and characteristic color.
A female should not be bred more than twice a year, since frequent “work” undermines her health and, as a result, her offspring will be weak and of poor quality. Uncontrolled use of males will also lead to unpleasant consequences - the potential mother will remain unfertilized.
A week before and during mating, animals are given food rich in vitamin E - sprouted wheat, barley, oats, as well as succulent food. The best time for reproduction is considered to be spring and summer, when there is a lot of varied food.
Obese, overly dense or thin, sick animals should not be allowed to crossbreed.
How to understand that pregnancy has occurred
In the early stages, it will be quite difficult to understand that the pet is in an “interesting” position, since they look as usual. Moreover, if a person is a simple hobbyist and does not breed guinea pigs, it will be impossible to understand this in the early stages.
But at the same time, the longer the period, the more signs are observed, they manifest themselves in habits and behavior. Already in the second month, you can notice external changes in your pet. Next, we will take a closer look at what changes occur in the life of a pet. Photos will help you navigate better.
Mating
For one male there should be from 5 to 10 female pigs. Some breeders keep them together, others separately - there is no fundamental difference. In the case of separate keeping, the female during estrus is placed in a cage with a “man”.
The hunt lasts about two days, the frequency of estrus is 13-20 days. The favorable period for fertilization lasts about 10 hours. The female takes a characteristic pose (she is motionless, her hind legs are apart, her croup is raised) and is ready to let her partner approach her.
Taking care of babies independently
In the event of the sudden death of a female or her refusal to care for the offspring, the best solution is to place the babies with another nursing female. Before this, the cubs are wiped with sawdust from the foster mother's cage. Additionally, it is allowed to treat babies with camphor oil to remove old odors. Having previously removed the female from the cage, foster ones are added to her natural cubs. Half an hour later the mother is returned and she takes care of all the babies as if they were her own.
If it is not possible to find a suitable pig, the owner feeds the cubs himself. Newborns feed every 2–3 hours, including at night. Feeding is carried out using a syringe without a needle or pipette. For food use 10% cream or dry milk mixture. After 5–6 days, night meals are canceled and the number of daytime meals is reduced.
On the second day, a bowl with dry rolled oats and pieces of vegetables is placed in the cage so that the cubs get used to adult food. In the second week, the diet changes to dairy-free porridge for children.
After each meal, the animal’s belly is gently massaged towards the tail. To do this, use a piece of cotton wool moistened with vegetable oil. This procedure stimulates bowel function and promotes bladder emptying. Under normal circumstances, the female licks the cubs' belly for this purpose.
Care during pregnancy
A pregnant guinea pig needs special care. She needs to be provided with complete rest. It is best to organize a special house for these purposes, where the animal could hide and subsequently hatch babies.
Pay attention to feeding the animal. Food should be complete, rich in protein and vitamins. It is recommended to give:
- green food,
- root crops,
- sprouted grain.
At the beginning of pregnancy, the amount of food is increased by 1/3, and at the end the female should receive twice as much food. Number of feedings up to four times a day.
Access to water is unlimited. The presence of fluid is especially important at the end of gestation, when the animal is very thirsty. Along with water, the expectant mother is also given milk; it should be warm.
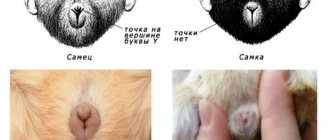
At what age do they give birth and how often?
These animals reach sexual maturity at a fairly early age. If we talk about the first mating, the best age is considered to be from 4 to 6 months.
The average duration of estrus is 16 days, but it should be borne in mind that there is a certain time period when the guinea pig is ready to mate and its duration is only 8 hours.
A female gives birth to 2-4 cubs. But soon she may again go into heat, in which she can also mate. Therefore, having cubs and feeding them, she may be pregnant with other offspring.
Pregnancy
Naturally, all novice pig breeders are interested in the question: how long do pregnant guinea pigs walk? So this period lasts differently for everyone: from 60 to 68 days. Much depends on the number of cubs. There were cases when, with a small litter, a pig carried offspring for 72 days.
You can tell if your guinea pig is pregnant by its enlarged belly and weight gain. Usually visual changes are visible on the 20th day from the beginning of fertilization. When palpating, an attentive owner can even “listen” to the movements of the fetus; they become more noticeable at the end of pregnancy.
During this period, the animal must be handled with the utmost care, since excessive anxiety will lead to abortion:
- you shouldn’t pick her up often,
- disturb you once again with inspections of the house or frequent cleaning,
- move the cell from place to place.
By the way, miscarriage or premature birth can be caused by an infectious disease - brucellosis. Therefore, even before mating, it is advisable to donate blood for analysis to a laboratory where they can detect or not detect antibodies for this disease.
Newborn guinea pigs: brief description, care features and recommendations
Guinea pig babies are unique in nature. While still in the womb, they can hear and see. The eye opening process occurs approximately 14 days before birth. When they come into the world, they can already see fully and very keenly hear all the sounds around them. But that's not all. At the time of birth, their incisors are already fully formed and ready for life, and this does not depend on the breed of guinea pig.
Despite such preparation for the future life, the baby will not have a chance to survive if his weight is less than 40 grams. Normal weight is considered to be 45 – 140 grams. The baby is born larger if he is alone in the litter. Accordingly, the more cubs in the litter, the smaller they will be and the less chance they have of survival. After 28 days, babies should be separated from their mother in separate places.
How does childbirth go?
Sooner or later, a guinea pig's pregnancy ends in birth. They are usually swift and pass at night. Before the cubs appear, the female prepares by arranging a nest. The babies are born one after another, the break is no more than five minutes.
Newborn guinea pigs are enveloped in membranes, which the female nibbles and eats. If for some reason the mother does not remove the membrane, it must be removed independently. Otherwise, the baby will suffocate.
If problems arise during childbirth, first aid is provided. The pig is massaged in the abdominal area, stroking movements are directed towards the birth canal.
Complications during childbirth
Usually childbirth is easy, but there are a number of cases when the help of a breeder and even a veterinarian may be required. Every guinea pig owner must know what to do in case of complications during childbirth and how to recognize life-threatening situations for the animal.
The most important thing is that the female’s birth canal should be completely open by the time labor begins. If the birth canal is open, the female has been pushing for a long time, but the cubs have not been born, she looks tired and depressed - you should immediately call the veterinarian. Most often, this situation requires surgical intervention.
Most often, complications during childbirth are caused by toxicosis during pregnancy. Toxicosis not only weakens the guinea pig's body, but leads to the death of babies. If toxicosis does not go away until birth, this can lead to the death of the female.
Another common cause of difficult births is the baby getting stuck in the birth canal. This can happen because the fetus is very large or the female is too old and her hip joint has lost mobility. You can identify a stuck fruit by the following signs:
- the female pushes for fifteen to twenty minutes, but the fetus does not come out,
- looks worried
- bites his sides.
In this situation, it will no longer be possible to save the fetus, but you can still help the female.
To do this, you should wash your hands well and examine the inside of the animal’s vagina with your finger. If the fetal head is detected, it should be squeezed with your fingers and gently pulled. It is better to do this simultaneously with the female’s attempts.
If a female once had complications of any nature during childbirth, then there is a high risk of their recurrence. The owner of a purebred animal or an animal of a rare color is more likely to risk re-coating, but in this case, during the next birth, the presence of a veterinarian is required. If the pig is outbred or is not of particular value, you should refrain from further producing offspring.
Baby care
After the guinea pig has given birth, there is nothing special for a person to do, since the mother herself is capable of caring for the offspring. Usually 1 to 5 cubs are born. Their weight is about 50-100 g (it all depends on the size of the litter), they are covered with hairs, have teeth, their eyes are open and in just a few minutes they can move independently.
The female has only two nipples, but they are quite enough to feed all the offspring - the newborns suckle in turns. From the third day, babies begin to try food for adult animals.
It is not recommended to pick up piglets immediately after birth. At one month of age they are placed in a separate terrarium.
If for some reason the pig refuses to feed the babies or she does not have milk, the cubs are transferred to artificial feeding or placed with another mother. Before this, the piglet’s fur is wiped with sawdust taken from the stepmother’s cage so that the latter can better accept the foundling.
You can also raise offspring using artificial feeding. To do this, newborns are administered 1 cc using a pipette. see baby formula every two hours for a week. They are also given hay and green food.
Do not forget to stimulate defecation and urination in orphans using a cotton pad, which is used to irritate the anal area.
Complications after childbirth
For females, fatigue after childbirth is normal. Some may not eat for several hours, but not a single guinea pig will refuse the offered favorite treat. If the female looks tired, does not eat, refuses treats, does not drink, and more than six hours have passed since the end of the birth, you should worry and call a specialist. Light bleeding is normal for the first few days, but heavy bleeding, especially on the third or fourth day, may be a reason to call your doctor.
One of the most common postpartum complications is mastitis. The main signs of infection are swelling and redness of the mammary gland, its hardness, and increased temperature. Most often, mastitis is accompanied by fever, loss of appetite, and apathy. First aid is expressing milk. With clean fingers, gently squeeze the nipple, and after a few drops of milk appear, wipe with a cloth soaked in a soapy solution, and then rinse with clean water. After pumping, it is recommended to massage the breast area for five to seven minutes.
Another common postpartum complication is hair loss. Childbirth and lactation lead to serious hormonal disturbances in the animal’s body and most often this affects the disturbance of the coat.
First, hair loss occurs in the sacrum area, then the back, legs, and neck of the animal become bald. Baldness is often accompanied by the appearance of wounds and cracks on the skin. The treatment is simple - washing with disinfectant solutions and lubricating the skin with any baby cream. Usually the fur begins to grow back without the use of any medications after two to three weeks.
Possible problems during breeding
- Death of offspring. It occurs for various reasons. One of the most common is that the mother does not accept the babies, which happens due to poor maternal instinct or lack of milk as a result of the stress of childbirth. It is better to cull such females immediately and not allow them to reproduce. Often a young mother herself can destroy her offspring due to excessive anxiety, when she endlessly drags them around in search of a safe place.
- Refusal to breastfeed. In this case, the mother is still kept close to the brood, but the babies are fed. After some time, the female can resume feeding. If there are problems with milk production, then it is better to discard such a mother and transfer the cubs to artificial feeding.
- Birth of stillborn piglets. The reasons are poor maternal feeding, vitamin deficiency, lack of micro-, macroelements or infection.
Breeding guinea pigs at home is not a difficult task at all, but even it should be approached with full responsibility, choosing the right breeders and providing comfortable conditions. Only in this case can you get healthy and full-fledged offspring.
Feeding
Newborn guinea pigs, already a short period of time after birth, can taste the food of adults. However, it is very difficult for a female guinea pig to fatten all her babies. One individual has only 2 nipples, which are very difficult to feed everyone. Therefore, quite often, one or more young individuals die. A week after giving birth, pigs begin to eat common food. Which allows them to gain weight.
Feeding with mother's milk occurs up to a month. After this, it is necessary to seat the offspring, distributing them by gender. If you do not have time to transplant males in a timely manner, you can provoke a recurrence of pregnancy, since at the age of one month, males are already considered sexually mature.