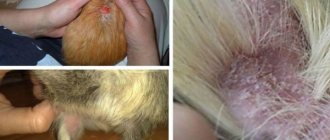
Domestic rats are clean animals, but they are not immune from infection by ectoparasites. If your rodent is constantly itching, you need to check its fur for crawling insects. However, some parasites are not visible to the naked eye because they are located under the skin.
Both species are extremely dangerous - they carry deadly diseases that can also infect people. Therefore, the owner of a decorative rat should know how to get rid of lice, ticks and fleas from his pet.
Ways of infection of rats with ectoparasites
Most often, rodents become infected with ectoparasites through direct contact with other animals - mice, dogs and cats. But there are other ways of transmitting parasitic diseases:
- Through infected inventory.
- Through the filler. Lice eaters and ticks can live in wood filler, which the owner buys not from a pet store, but from a sawmill. Such material does not undergo processing, which means it may be contaminated.
- Often the person himself brings lice eaters and other ectoparasites into the house on his clothes or shoes. After some time, they find their prey (pet) and begin to reproduce.
Lifestyle
Bloodsuckers cannot remain on the victim’s body all the time. After eating, the flea jumps off and returns to its permanent habitat. They often settle in rat nests and lay eggs here. People know that pets have blood-sucking parasites, but do rats have fleas? They are present in all living organisms, even in humans, but are called a little differently. Females can produce up to 400 of their own kind. They lay 7 eggs per day. The development of the larva takes up to 16 days, then is wrapped in a cocoon.
An adult flea emerges from the pupa. Can go without food for a long time. But then, when it chooses a suitable victim, it will suck blood for a long time.
Main ectoparasites of rats
Decorative rats are affected by several types of parasites. These include:
- mites;
- lice eaters;
- fleas.
The listed types of ectoparasites do not live on humans, but some can bite humans. Fleas and lice eaters, as well as the rat mite Ornithonyssus benoiti, are carriers of infectious diseases. They often become the cause of worm infection. Therefore, if you suspect the presence of ectoparasites in a domestic rat, treatment should be started as quickly as possible.
Ticks
These parasites belong to the order Arthropods. Several types of mites infest rats:
- cutaneous Radfordia ensifera;
- scabies Notoedres muris;
- sarcoptoid Sarcoptes anacanthos;
- subcutaneous Demodex.
Unlike lice eaters and fleas, such parasites cannot be seen with the naked eye. Firstly, because they are embedded in the skin. Secondly, rat mites are small in size - from 0.3 to 0.6 mm.
The main symptoms of infection are baldness and incessant itching. When a rat mite bites through the skin, the rodent experiences pain. Then the puncture site begins to itch. The rat bites itself and tears its body with its paws. Over time, she becomes nervous and loses her appetite.
Wounds and crusts appear on the skin, which are concentrated in the head, neck, shoulders and ridge. Some people think it's an allergy, but rats are omnivores and rarely suffer from food intolerances. Therefore, if symptoms of scabies appear, you should take your pet to the veterinarian and take a skin scraping.
Attention! Rat ticks Ornithonyssus benoiti are dangerous to humans. They cause severe dermatitis and transmit infectious diseases - tick-borne encephalitis, icteric leptospirosis, tularemia and Lyme disease.
Lice eaters (lice)
Most often, rats suffer from head lice. This disease is caused by lice - blood-sucking lice Polyplax spinulosa. They live in the animal's fur and feed on blood, secretions of the sebaceous glands and skin cells.
Lice eaters in rats can appear after contact with a sick animal. The owner may also be involved in infesting the pet with lice. Parasites can be on shoes or clothing. Also, a domestic cat or dog can bring lice eaters into the apartment on its fur.
Rat lice are small insects with elongated bodies that are yellow or light brown in color. Its dimensions do not exceed 1 mm. The lice eater has 3 pairs of limbs. The head has a piercing-type mouthparts. With its help, the louse pierces the skin to get food. During a bite, she injects a special substance into the dermis that prevents blood clotting.
The female lice eater is slightly larger than the male. She produces up to 60 eggs at a time. Nits attach to the hairs of the fur at their base, right next to the skin, because it is warm there. The eggs of lice eaters hatch into larvae, which then molt three times and turn into sexually mature individuals (imago). The full development cycle of the parasite occurs within 3-4 weeks.
The incubation period after lice infection until the first symptoms appear in a rat can last about 30 days. When a lice beetle lands on a rodent's body, it attaches itself to the hairs using mites that are located on the parasite's legs. The louse burrows into the rat's skin and begins to drink blood. A secretion from the salivary glands of the lice eater gets into the bite site. This liquid irritates the skin and causes itchy spots and nodules to appear.
Parts of the body on which rat lice infest:
- head;
- withers;
- parotid region;
- neck;
- area around the anus.
At an early stage, lice eaters in rats with dark fur are quite difficult to detect, since there are few of them and they blend in against the background of the fur. In rodents with light coats, mature lice are clearly visible. They are located on the skin and resemble moving red dots.
In dark-colored pets, it is easier to detect lice eggs. They are oval in shape and whitish in color. Nits are not found on the skin, but on the hairs of the fur.
Symptoms of lice beetle infestation:
- the rat itches frequently;
- scratches and reddish spots appear on the skin of the muzzle, neck and shoulders;
- the fur begins to fall out;
- the animal becomes irritable and loses appetite;
- The rat is losing weight.
Important! Lice eaters do not attack people, so they do not pose any danger to the owner of the rodent.
Fleas
Fleas are very rare in domestic rats. These parasites can use the rodent as a temporary source of food.
Like lice eaters, rat fleas live on the surface of the skin. They also feed on blood. The parasite's body is flattened on the sides, which allows it to move deftly and quickly in the thick hair.
The flea has a head and a rounded abdomen equipped with a piercing-sucking mouthparts. The entire body is covered with a durable chitinous layer with bristles; it protects the parasite from mechanical damage. The flea has 6 long limbs, thanks to which it can jump up to 1.5 m. Each leg consists of 5 segments.
Parasites do not live on the animal's body, but use it only as a source of food. They lay eggs in hard-to-reach places - behind the baseboard, in cracks on the floor. The flea is larger than the lice eater. The size of its body varies between 0.5-1 mm. The parasite is colored brown.
You can detect fleas in a rat by the following signs:
- the rodent becomes nervous and itches;
- his coat is thinning due to mechanical damage to the skin;
- bite marks appear on the body;
- adult parasites that move quickly can be seen in the fur;
- If you part the fur of a rat, it will contain arthropod excrement - brown lumps that look like poppy seeds.
Important! Fleas can bite people. They carry diseases dangerous to humans - some types of helminthiasis, tularemia, listeriosis, plague, brucellosis, typhus and encephalitis.
Appearance
These insects are divided into varieties; the most common type of flea is the southern rat flea.
With the naked eye it is impossible to distinguish them from other relatives - dogs, cats and domestic ones. Only a specialist can determine the species under a microscope.
The rat flea looks similar to other representatives of the genus: the body has an elongated shape, flattened on the sides, the back part is raised due to long jumping limbs.
It is covered with chitinous cover and has a dark brown color. Length – from 3 to 5 mm.
Treatment of external parasites in rodents
If you suspect a rodent has been infected with any type of ectoparasite, consult a veterinarian. The doctor must examine the animal and advise how to treat it. The fact is that some medications are suitable for killing subcutaneous mites in rats, while others are used for fleas and lice eaters. Acaricidal preparations act on arthropods, and insecticides act on insects. However, there are complex medications that simultaneously act on fleas, lice, ticks and even helminths.
Parasites in rats are easily treatable. The main thing is to choose the right drug and calculate the dosage correctly.
List of medications for ectoparasites for rats based on selamectin or fipronil in the form of drops on the withers:
- Stronghold;
- Advocate;
- Frontline;
- Leopard;
- Fiprist;
- Delix-F;
- Dana.
When purchasing a drug for lice eaters and other parasites, you should give preference to medications that are intended for puppies and kittens. The fact is that veterinary pharmacies do not sell insecto-acaricides specifically for rats.
The dosage and treatment regimen should be announced by the doctor. If your pet is concerned about rat mites, your veterinarian may recommend an injection of Ivermectin. It is administered subcutaneously 3 times with an interval of 10-14 days.
In case of complications in the form of suppuration on the skin, the treatment regimen includes antiseptics, antibiotics and healing ointments. The rat should receive a diet rich in vitamins to strengthen its immunity. The sick rodent is isolated from other rats. The old bedding is thrown away, the cage and all equipment are disinfected.
Attention! If fleas or lice eaters are found on a rat, you will have to treat other pets as well, since there is a high probability that they brought the parasites into the house.
Composition and effect of the drug
The product is available in the form of a concentrated emulsion. Before use, prepare a solution in the dosage specified in the instructions. The concentrate must be diluted immediately before use, or at least within 2 hours after preparing the solution. Under other circumstances of use, the drug loses its effectiveness.
The active components are new generation synthetic insecticides:
Preventive measures
Prevention of infection of a domestic rat with ectoparasites includes the following measures:
- use of high-quality litter fillers;
- limiting the contact of the rodent with other pets;
- sending new animals to quarantine for a period of at least 2 weeks;
- regular cleaning and disinfection of cages and equipment;
- washing shoes after being outside;
- strengthening the immunity of the domestic rat.
Ectoparasites are very dangerous, so it is important to detect signs of infection in time. Every pet rat owner should regularly examine their pet for scratches and wounds on the skin. If they exist, it is worth showing the animal to a veterinarian and, if necessary, starting treatment.