- home
- Guinea pig
- Guinea pig health
02/07/2019 Scratching from time to time is a natural urge of any living creature. But this desire is not always caused by a harmless reason. The pet may get sick or “catch” parasites. Scabies leads to the formation of bloody wounds, due to which the body easily succumbs to infections. It is important to learn to distinguish normal scratching from a dangerous symptom in order to provide timely help to the animal.
What should be of concern
Usually a guinea pig scratches to tidy up its fur or to soothe a slight itch. However, you should be wary if the animal constantly scratches the same place or bites itself. Warning signs include:
- Formation of bald patches (not counting the natural lack of hair behind the ears and on the inside of the front paws);
- depressed or restless state of the pet;
- loss of appetite;
- strong thirst;
- dry skin, dandruff;
- formation of scratches, crusts, ulcers;
- inflammation of skin blood vessels.
Often the reason is visible to the naked eye - there are parasites in the fur, such as mites or lice. Sometimes the problem lies in internal pathologies of the body - vitamin deficiency, allergies, intestinal parasites.
Stress
Stress can cause problems with the nervous system, so the guinea pig will begin to itch, lose hair and lose appetite. There can be many reasons for this little animal's stress. One of the main ones is poor living conditions, due to which the guinea pig is constantly in an uncomfortable and irritable state. Stress can accumulate and result in serious health problems.
If a guinea pig chews on the cage, then the cage is too small for it: these animals are not that small, and therefore require space.
Cause: Parasites
Skin parasites are often the reason why a guinea pig itches. As a rule, they are easy to spot with a magnifying glass. The most common of them:
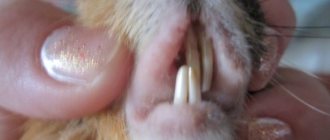
- Scabies mites. They settle under the skin on different parts of the body. To detect it, you need to take a scraping from a veterinarian and send it for analysis. Treatment consists of subcutaneous injections of Ivermectin or external treatment of the affected areas of the skin with Novomek or Otodectin.
- Vlaseaters. The parasite is easy to notice - its length reaches 1.5 mm. Lice eaters feed on hair follicles, blood and skin particles. A distinctive feature: the parasites gnaw the hairs at the base, which is why bald spots form on the animal’s body. For treatment, use Stronghold drops (for kittens).
- Lice. They become the cause of a disease called pediculosis. They usually live on the head and ears. At an early stage, it is possible to get rid of lice by carefully combing the fur with a thick comb. In the later stages, the drug Ivermectin helps.
- Fleas. In some cases, multiple bites cause anemia. They are removed by various drugs containing permethrin.
Despite the difference in appearance, the parasites cause similar symptoms: the pig jumps and itches, its hair falls out, and its appetite worsens. The skin peels and dandruff appears. It is important not to delay treatment, otherwise the pet will scratch itself until it bleeds, and a dangerous infection will get into the open wounds.
Parasites appear due to low-quality feed, hay and grass, the producers of which violated storage conditions, from dirty water, from other animals and people. Therefore, even if your pet does not go outside, you should not discount the possibility of ticks or fleas.
If skin parasites occur, the cage and objects used by the pig should be sanitized. All pets and family members are checked just in case.
In addition to external parasites, pigs are also attacked by internal ones - worms. Symptoms of helminths: weight loss, lack of excrement. But in some cases, itching may occur and, as a result, hair loss.
Not enough vitamins
Symptoms of vitamin deficiency are similar to signs of parasite infection:
- Hair loss;
- apathy;
- skin rash;
- constant itching.
If the presence of parasites is not visually detected, and tests show the same, the cause of scabies in a pig may be a lack of vitamins. This often occurs in spring and autumn when air temperatures are unstable. Vitamin deficiency also appears after a serious illness or from a lack of succulent food in the diet.
Treatment is not difficult: the pet is given pharmaceutical vitamins or food containing vitamin C (for example, parsley). It is allowed to add ascorbic acid to drinking water (1 mg per liter is sufficient). Until complete recovery, the pet is placed in a warm place so that it does not get a cold, which, against the background of vitamin deficiency, will develop into pneumonia.
Bad habits
There is another reason why an animal scratches and bites: boredom. Pigs are social animals and prefer the company of their peers or other pets. Therefore, they are usually included in homosexual pairs, unless there is an intention to breed or spend money on sterilization. If it is not possible to keep two pigs (they will need a larger cage), you should buy rodent accessories for your pet or increase the number of walks in the fresh air.
There are many reasons why a pig may experience itching and hair loss. None of them will leave on their own. The owner’s task is to notice these symptoms in time and determine their cause. Your veterinarian can help you make a diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment. Also, do not forget about preventive measures to maintain the health of your pet.
Allergic pig
Itching often accompanies a disease such as allergies. The pig itches, coughing, watery eyes, sneezing, and swelling of the eyelids. Allergies usually occur to food or bedding material (especially pine sawdust). If a pet has been eating the same food and sleeping on the same type of sawdust for many years, over time it may develop intolerance to these products.
Allergies cannot be cured. But in order to remove the symptoms, the animal needs to change food or bedding material. To determine what makes a guinea pig itchy, they are offered different foods one at a time. Symptoms appear a couple of minutes after contact with the allergen. Additionally, the pet is given antihistamines. In addition to food and sawdust, allergies are caused by tobacco smoke, dust, and pollen.
Dermatophyte is a fungus
Dermatophyte is a fungus that causes lichen. It forms on the muzzle, then spreads throughout the body. It appears as round, inflamed areas of baldness. If left untreated, the zones expand and merge with each other. The animal itches until it bleeds and ulcers and ulcers form on the skin. The risk of developing a secondary infection, which can be fatal, increases.
Causes of lichen:
- Heat;
- humidity;
- advanced age;
- stress;
- wet litter;
- contact with a sick animal;
- eating disorder.
Sometimes the fungus becomes a symptom of another disease, such as a mite infestation. Therefore, if it occurs, it is better to show your pet to a veterinarian. The doctor will scrape the skin, accurately determine the disease and prescribe appropriate antifungal medications.
Stress
Guinea pigs are small and shy animals. Many factors cause them stress:
- A change of scenery;
- sudden movements;
- loud sounds;
- physical injuries;
- prolonged contact with people or animals.
It doesn't matter whether the pet is afraid or irritated. For such a small animal, strong experiences have a negative impact on health. He is going bald, losing his appetite, jumping nervously and itching.
Lichen
The guinea pig constantly scratches itself and goes bald when the skin is affected. Pathogenic fungi cause trichophytosis and microsporia, collectively referred to as “lichen.”
Sick animals pose a danger to humans and their relatives.
For pathology:
- on the skin of the animal around the eyes, nose and limbs, characteristic outlined round inflamed areas of baldness form;
- The rodent often scratches itself, becomes restless and chews its fur.
In the absence of timely treatment:
- the affected zones enlarge and merge;
- the animal is rapidly becoming bald;
- the skin becomes covered with ulcers and ulcers;
- weak individuals and young animals may die from secondary infection.
Bald circles with microsporia have characteristic outlines
What to do if a small pet has lichen spots on its head and limbs?
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out in a veterinary clinic; irradiation of the affected areas with a Wood's lamp and microscopic examination of skin scrapings are used to identify the pathogen. To treat a sick animal, antifungal drugs are prescribed; the duration of therapeutic measures and the outcome of the disease depend on the severity of the pathological process.
Prevention
First of all, you should follow the rules of pet care and hygiene: feed fresh food, regularly wash the cage and bowls, and monitor the cleanliness of the room in which the cage is located.
The animal is periodically checked for pathological abnormalities. If a pet suddenly becomes bald and itchy, the owner will immediately notice it and will be able to provide help in time.
Pigs often pick up parasites from other animals. If there are other pets living in the house, their health must be monitored. It is recommended to keep a newly purchased pig in quarantine for some time and not allow it to the rest. A sick pet is isolated from healthy ones - the infection spreads quickly.
Features of correct content
A common reason why a guinea pig often itches is a violation of the conditions of detention. If you follow the care recommendations, the animal lives up to 8 years.
The animal should be provided with a spacious cage of at least 40x80 cm in size and 50 cm in height. A cramped home leads to a depressed state of the pet. The cage itself is placed away from sources of draft, direct sunlight, batteries, and TV.
The pet's diet consists of solid and succulent food in equal proportions to avoid digestive problems. Additionally, they offer vitamin and mineral supplements, hay, and some vegetables. Food bowls along with the cage must be washed at least once a week to avoid the accumulation of germs.
Physiological molting
In the first case we are talking about normal molting. Molting in warm-blooded animals is the process of changing fur or feathers.
There are three types of molting:
- Juvenile or age-related – the “childish” coat is replaced with an “adult” one.
- Seasonal – occurs in connection with the change of seasons. Seasonal molting is “triggered” by changing air temperature and weather conditions.
- Compensatory – occurs due to damage to the coat by any physical impact (trauma, thermal or chemical burn, etc.).
When a guinea pig sheds, its epidermis renews itself. The skin thickens, becomes looser, and therefore more vulnerable. Therefore, your guinea pig needs to be supported during this period.
Juvenile coat change occurs only once in a lifetime. During this period, “children’s” fluff is replaced by “adult”, coarser and heavier wool. The animal then lives with this fur throughout its life.
Guinea pigs shed seasonally twice a year, just like most other mammals.
In autumn, the guinea pig sheds from September and this shedding usually does not bother her. Spring shedding occurs in March, and it is an order of magnitude more hassle than autumn shedding.
This is due to the fact that during the winter the pig does not receive enough green food (grass, vegetables, fruits), and with it the necessary vitamins and amino acids. To facilitate the molting process, you need to constantly monitor the completeness of your animal’s diet.