- home
- General information
23.03.2018
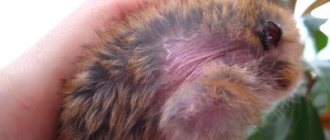
Before you go to the store to buy a hamster, you need to know about the health of the animal. This will help you avoid buying a sick animal and help you be on guard. After all, if you buy a sick pet and don’t know about it, it can die within a month after purchase. Serious diseases include a wet tail in a hamster. When choosing a pet, pay attention to its backside. Sputum may indicate illness.
Risk factors
Hamster breed
Any rodent can experience severe diarrhea, but some breeds are not susceptible to ileitis. For example, dwarf hamsters.
Among patients with “wet tail”, Syrian rodents with long hair are often found. When choosing a hamster breed, study its characteristics, including propensity and ileitis. It would be a good idea to consult with the breeder and veterinarian.
Extra attention
Desulfovibrio is a bacterium that often affects young hamsters under 8 weeks of age. Weak immunity is not able to resist the pathogen. It is worth paying attention to the health of a small animal before buying it from a nursery.
Handling is dangerous
Severe stress can trigger the appearance of a “wet tail.” This often affects young rodents that are taken from their mother before the age of two months. Strengthening the immune system of a young hamster occurs within a week in a new family.
Important! When buying a small animal, do not rush to handle it often. The hamster will need time to adapt.
Gastrointestinal diseases
Ileitis in hamsters occurs as a result of E. coli entering the body. Common reasons:
- poor quality food;
- non-compliance with terms and conditions of its storage;
- irregular replacement of water in the drinking bowl;
- wet and untreated litter.
Such conditions provide a favorable environment for the development of bacteria.
Wet tail is a consequence, not a cause
At best, severe diarrhea may be due to a less serious illness. However, ileitis is difficult to treat even under the supervision of a veterinarian.
The first symptoms should be a signal to contact a veterinary hospital. It will take a lot of time and effort to save a pet.
Why does a hamster need a tail?
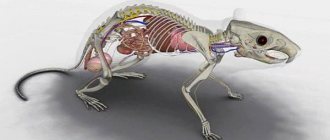
The hamster is one of the miniature representatives of the rodent family. Before getting a pet, it is very important to study its anatomy. This way you can better understand how to care for it without causing damage to your health. The animal has a fragile body structure, so it must be carefully supervised.
The anatomy of a hamster is similar to other mammals, but there are some differences.
Symptoms of the disease and methods of diagnosing it
The main danger of the disease is that the latent period can last several weeks, so you can buy an already sick animal whose disease is in the incubation period. Hamsters aged 3-8 weeks are most vulnerable to the disease.
“Wet tail” is the name used among the people. In professional language, bacterial
the infection will be called proliferative ileitis, since, first of all, the ileum suffers from it. The animal begins to have diarrhea: first it is watery discharge, and then bloody discharge, which has a characteristic foul odor. The back of the hamster is wet, which is why the disease has earned its popular name. Often the animal experiences rectal prolapse, because the intestines constantly suffer from spasms. Diarrhea leads to dehydration, and in this condition the rodent can live no longer than three days. The disease can be diagnosed only by clinical symptoms.
The incubation period can last 10 days. There are clinical signs of “wet tail” in hamsters:
- severe diarrhea with a strong odor;
- blood appears in diarrhea;
- the animal sits hunched over;
- the fur is tousled, the shine of the coat has disappeared;
- restless and aggressive behavior.
Due to abundant liquid secretions, the back of the body becomes wet. The animal is severely dehydrated. Loss of appetite leads to sudden weight loss.
Symptoms of proliferative ileitis:
- Prolonged lack of appetite;
- Weakness, apathy, drowsiness;
- Change of behavior to aggressive and cruel;
- Wet back of body due to constant diarrhea.
Isolate your sick hamster
Ileitis is a contagious infectious disease. To prevent other pets from catching the disease from a sick hamster, it is better to house the rodents during treatment.
Important! The infection spreads not only due to direct contact between hamsters. A healthy animal can become infected from a sick animal through the owner’s hands, toys and other objects.
The right decision would be to temporarily transfer custody of healthy rodents to a family friend. This measure will help prevent the spread of the disease.
Restore your pet's water balance
Severe diarrhea causes the hamster to lose moisture from its body. The animal refuses to consume food and liquid.
Check the degree of dehydration as follows. The owner needs to carefully feel the withers behind the ears of the small animal with his fingers. If the fold straightens out immediately, then the fluid content in the body is considered acceptable. In a sick hamster, the skin fold very slowly returns to its previous shape.
Injections are the fastest and most effective method of combating dehydration. The owner can independently inject under the skin, but intra-abdominal administration of drugs is performed only by the hand of a veterinarian. The following drugs are used:
- ringer's lactate;
- 9% saline;
- 5% glucose solution.
The dose is prescribed by the veterinarian according to the weight of the sick hamster.
Treat your pet at home
When the first symptoms of a “wet tail” appear, the responsible owner is faced with the task of reducing diarrhea. Cereal decoctions are suitable for this.
Important! Cereal decoction and other folk methods only temporarily relieve the rodent from severe pain and diarrhea. Self-medication at home does not lead to recovery. The entire incubation period must be supervised by a veterinarian.
Keep your hamster warm
Small mammals are characterized by a high ratio of the body surface to its mass. Therefore, sick hamsters are prone to severe hypothermia. This condition poses a danger to a weak body.
The optimal temperature for a hamster in a room is 21-26 0C. The owner should prevent the appearance of drafts in the place where the cage with the sick animal is located. The litter must be clean and dry.
Reduce stress
While the animal is under the care of a veterinarian, its owner can contribute to a speedy recovery. To do this, you need to eliminate possible stressful situations in this way:
- do not move the rodent unnecessarily (only to the veterinary hospital);
- even an isolated animal should have a secluded place to rest;
- the hamster must sleep at any time of the day, for this reason family members try not to make noise near the cage;
- A recovering pet will want to climb and dig again; you should not deprive him of this opportunity.
To restore strength, the hamster will need time, silence and a calm environment.
Hygiene
The disease will progress if:
- do not change the litter;
- do not monitor ventilation and humidity in the room with the cage;
- keep your diet the same.
Disinfection of the cage is a mandatory measure when identifying ileitis in a hamster, because the infection spreads through secretions.
If a sick hamster dies and a cage remains behind, then you need to replace all possible parts of it:
- drinking bowl;
- feeder;
- sunbeds;
- ladders and other equipment.
What remains is treated with a disinfectant solution. Any detergent that contains chlorine will do. Then the cage is rinsed generously with water and ventilated. Such measures will preserve the life and health of the new pet.
Be prepared to make a difficult decision
“Wet tail” in most cases cannot be treated. Animals that survive the disease acquire immunity, but complications with the digestive system are possible.
If treatment started on time does not improve the pet’s condition, then you need to be ready to let him go. It is important that the animal is given a chance.
Eliminate fruits and vegetables from your pet's diet.
Changing your diet can feel like new stress for your hamster. The incubation period requires avoiding vegetables, fruits and other watery foods that will contribute to diarrhea. Dry food will ease the animal's condition. A diet of grains (wheat, oats and wheat) will strengthen the stool. When using ready-made mixtures, you need to make sure that they do not contain any suspicious additives.
Anatomy of the Djungarian hamster
The Djungarian hamster can be distinguished from the Syrian by the presence of hair on the limbs, by the color of the hair, and by the gray stripe that runs from the head to the tail. The Dzungarian hamster grows up to 10 cm in length, and the Syrian hamster up to 20 cm. The Dzungarian hamster bears the fetus in 19–22 days, and the Syrian hamster in 16 days. In the female, the uterus is divided into 2 parts.
Hamsters have identical ears. They perform the functions of hearing, coordination and maintaining balance.
Methods of treating the disease
IMPORTANT! We advise you to consult a veterinarian rather than follow advice from the Internet. Always remember that such articles may not be written by DOCTORS.
Eliminating the pathogen
Wet tail is an intracellular bacterium, so you need to resort to an antibiotic that can penetrate the cell and destroy the pathogen. Medicine for hamsters must be selected carefully so that the drug does not have a toxic effect (many antibiotics that are suitable for treating rodents cannot be used on hamsters).
Human medications can be used for treatment - oral suspensions. You can take Biseptol, which combines two active ingredients.
Also, most often, therapy is carried out using Baytril 2.5% (administer 0.4 ml over the skin of the animal per 1 kg of live weight). For a small rodent weighing 250 g, 0.1 ml is enough. Usually the antibiotic is injected once a day for a couple of weeks, and in difficult cases - twice a day.
Dehydration
The cause of death is dehydration, which occurs quite quickly with profuse diarrhea. Trying to give the hamster water is useless, since the liquid will not stay in the cells after passing through the digestive tract. The bad news is that rodents are too small, so intravenous injections are contraindicated for them. The best option for hamsters is intraperitoneal and subcutaneous injections. The owner can inject himself under the skin, but only a professional should inject into the stomach.
For injections, Ringer's Lactate is used, but you can use regular saline as an alternative: for 1 kg of live weight you need to take 40 ml of liquid. At the same time, you will need to inject glucose: 5% of the drug is injected into the body 2-3 times a day. To strengthen the immune system, vitamin C and Catozal are used together with the above drugs.
Treatment should be carried out in a well-washed cage, and hygiene procedures should be constant. When the rodent has completely lost its appetite, you can feed it manually: it is fed with baby formula (without milk protein) from a pipette or insulin syringe. Any succulent food should be excluded from the diet, but care must be taken to ensure that there is no significant loss of water.
Conditions of detention before recovery
The cage needs to be washed every day and the bedding changed to provide a warm and dry environment for the pet and to prevent re-infection of the animal. Juicy food must be completely excluded from the diet.
Proliferative ileitis is a difficult disease that cannot often be cured, even if proper and timely therapy is provided. If treatment attempts are completely excluded, then in 90-100% of cases the rodent dies. Owners can be quite principled when it comes to treating their pets. They exclude antibiotics because of the great harm they cause to the liver, and they consider injections to be a great stress that can kill the hamster. But the real danger comes from the disease, and antibiotics and injections are the only chance for salvation.
Anatomy of the Syrian hamster
A distinctive feature of hamsters is the presence of cheek pouches. They are located on both sides of the jaws. The bottom of the pouches is located near the shoulder joint. They use them to carry food to secluded places. If the pet completely fills these bags, its head will double in size. It extracts food from its cheek pouches using its paws. The bags can hold 18 g of food or more.
The animal can use its cheek pouches as defense. If danger approaches, he inflates them with air, which makes them seem scarier.
There are 16 teeth in the oral cavity. Of these, 12 are molars for chewing food and 4 are incisors. A characteristic feature of the rodent family is the absence of fangs. There is a void (diastema) between the incisors and chewing teeth.
The animal's incisors are constantly growing, so it is necessary to give the pet wooden objects and solid food. If the incisors are not ground down, they will reach large sizes. Then it will be difficult for the animal to close its mouth and chew. Subsequently, you will have to contact a veterinarian for an operation to shorten the incisors.
The hamster's skeleton is identical in structure to other mammals, but the bones are very fragile. If the animal jumps or falls from a height, it will break limbs and may damage internal organs. Hamsters are active animals; they love to climb heights, so they often have broken legs.
The structure of the internal organs is similar to other animals. A distinctive feature is the structure of the stomach (two-chamber), consisting of 2 sections:
- The function of the front is to soak food.
- Digestion occurs through the glandular section.
The distance from the anus to the genitals will help determine the sex of the animal. In females it is 3 mm, in males it is from 1 to 1.5 cm.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional methods can be quite effective in treating human diseases, but with animals the situation is different. Not all recipes that help people are suitable for animals, so you need to be very careful. If you are sick, it is better to consult a veterinarian, but if this is not possible, then you can try using a decoction of grain crops (barley and oats are most often used). This remedy will help stop the diarrhea, and then there should be enough time to take the patient to a veterinary clinic. Traditional methods are aimed at eliminating symptoms and gaining time, and not at fighting the cause.
What does a hamster look like?
The family includes small, tightly built animals with short but developed body parts.
The body length of hamsters depends on the specific species and sex and can be from 7 to 35 cm. The length of the tail usually does not exceed 10 cm. Sexual dimorphism in size is widespread in hamsters (females are often larger than males). The back color varies from off-white to brown, and the belly color ranges from white to black. You can find individuals with a pronounced black stripe running across the entire back. Some species of hamsters have distinct pouches for carrying food.
In this article we will take a closer look at the physiology of the most popular hamster species. Interesting? Read on!
Anatomy of the Syrian hamster
One of the main features of this type of hamster is the presence of cheek pouches designed for carrying food to the place of residence, while the mass of food carried can reach 18 grams, and the size of the head can double in size - these are the capacious pouches.
Hamster jaws consist of self-sharpening incisors for obtaining and molars for chewing food. It should be noted that self-sharpening incisors are constantly growing, so it is necessary to provide the hamster with hard objects when keeping it at home - branches, unpainted wood or a special mineral stone.
The stomach of hamsters consists of two sections: the first section is responsible for softening food before it enters the second section, and the last section is responsible for digesting food and pushing it into the intestines.
The sex of a hamster is determined by the distance from the anus to the genitals: for males this distance is from 1 to 1.5 cm, and for females it is an order of magnitude smaller, the distance is practically not noticeable.
Other possible explanations
As with any illness, your hamster may have symptoms similar to a wet tail without the wet tail. It is important to be very clear with your veterinarian and have the animal tested.
- UTI (Urinary Tract Infection): This most often occurs in older female hamsters, but can happen to any hamster of any age. Symptoms include: blood in the urine, smelly urine, dirty yellow or brown spots around the genitals, ruffled fur, excessive drinking, fatigue, loss of appetite, squeaking when going to the toilet.
- Uterine Problems: Only occurs in female hamsters, especially older ones that have been bred. Symptoms include: bleeding around the genitals, a smelly metallic brown or yellow discharge, a swollen or lumpy belly, a protrusion from the genitals, such as something loose, symptoms that do not improve with antibiotics. Your hamster may appear bright and healthy. Possible options include infection, obstruction, tumor, injury, or labor problems.
- Poor nutrition: This can result in a soft, sticky or running tail without a strong odor or symptoms of a wet tail. There may be diarrhea in the cage, and the hamster may be quiet with loss of appetite, but it is usually not that severe. This may, however, result in a wet tail. Cut back on greens and give them only as treats and do not feed your hamster human foods.
- Sitting in your own mess: Typically causes stains or a wet urine smell/sticking to the hamster that is not runny or soft. Your hamster will likely smell and improve after drying off with a baby wipe and cleaning the cage thoroughly.
Features of the sense organs of hamsters
Vision
Are the hamster's eyes, like those of other rodents, located on both sides of the head? which provides a wider viewing angle. This feature of the hamster’s head anatomy significantly eliminates its myopia. It is worth noting the peculiarity that the light sensitivity of the eyes is much higher than that of a person, so keeping a hamster on a windowsill or in a bright room without the use of a darkening cape is not recommended.
Contrary to popular myth, hamsters are not colorblind. The range of color perceptions of this rodent ranges from light yellow to dark blue.
The hamster's ears are quite mobile. Hearing is more acute than that of humans. In addition, this species of mammal is capable of detecting ultrasound.
Smell
Like many other rodent species, the hamster receives most of its information about the world around it through its sense of smell. The main role in the sense of smell of hamsters, as well as in the sense of smell of many other animals (dogs, cats), is played by whiskers - whiskers. With their help, hamsters navigate in burrows and find food.