- home
- General information
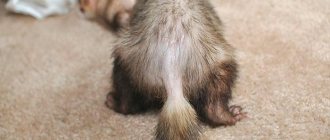
11/04/2018 Coprostasis, or constipation in a hamster, is a digestive failure, expressed in difficulty in defecation or regular incomplete bowel movements. This is an extremely dangerous condition for little furbabies. It causes intoxication, the appearance of fecal plugs, intestinal prolapse and can result in the death of the animal. Therefore, coprostasis requires urgent treatment.
What to do if your hamster is constipated
Every day the charming hamster cheers up its owner and goes into his arms.
Suddenly, the affectionate rodent becomes extremely restless and its abdomen swells. What should an owner do if a hamster is constipated? It is necessary to help the animal cleanse its intestines; constipation can cause poisoning of the body, the formation of coprostasis, rectal prolapse from the anus and death. It is usually the owner's fault that a hamster does not poop. If a rodent does not have access to drinking water and eats a lot of dry food, then it gradually develops constipation. Fiber is a biological causative agent of peristalsis; it is found in buckwheat, couscous, oatmeal, corn, fruits and vegetables. An unbalanced diet is the main cause of this unpleasant disease. Sometimes a hamster does not have bowel movements due to anxiety, various diseases of the small and large intestines, and mechanical damage.
Hair loss and other diseases of hamsters
Dandruff, scratching and baldness in hamsters can be caused by ectoparasites, pathogenic dermatophyte fungi, endocrine system disease, and sometimes tumors. The severity and duration of skin diseases in hamsters depends on the cause.
Many of these diseases, such as dermatophytosis or lichen in hamsters , are contagious and can be transmitted to humans. Therefore, if you notice suspicious symptoms, immediately take your hamster to a veterinarian.
Hamsters are often troubled by Demodex , which can be transmitted from one hamster to another. Only a veterinarian can identify the cause and prescribe the correct treatment.
Abscesses are an accumulation of pus in a limited cavity. Pus accumulates under the skin, sometimes forming large, painful swellings on the surface of the hamster's body. Abscesses can form due to cuts and scrapes in the skin. If sharp food particles injure the wall of the cheek pouch, a cheek pouch abscess may develop, and the cheek will appear full all the time. Abscesses require treatment by a veterinarian.
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis is a disease of viral etiology; it can be asymptomatic in hamsters, but there is a danger of infection in humans. When buying a hamster for a child, remember the possible risks; conduct a preventive examination of the animal by a veterinarian.
Causes of constipation in a hamster
Typically, intestinal dysfunction in hamsters develops due to the fault of the owners. The reason is insufficient intake of moisture and fiber. Thus, constipation is primarily caused by excessive consumption of dry food and insufficient drinking water. Fiber starts the digestion process. It is found in vegetables, fruits and grains. The lack of such food in the animal’s menu is the root cause of the development of the disease. Less common factors are stress, trauma and intestinal pathologies.
Injuries in rodents
Injuries, bruises, fractures in rodents
Can occur when falling from a height or improperly restraining the animal. Sometimes tissue or limbs are pinched. Injury is caused by using cotton wool as bedding instead of hay or sawdust. Lameness that progresses to complete impairment of limb function can result in self-amputation of the paw, especially in hamsters and rats.
Fractures and cracks of bones in rodents
They can happen while playing with children or fighting among themselves, when the cage door is quickly slammed shut. Characteristic signs are that the animal squeals in pain, swelling of the limb, lameness, and hematoma appear. With an open fracture, the bones break through the soft tissue and come out. It is necessary to immediately limit mobility, transfer the rodent to a small box or carrier, and take it to a veterinary clinic for treatment. Bites and wounds occur as a result of a fight with another animal. The wound should be washed with an antiseptic solution (for example, an aqueous solution of Chlorhexidine 0.05%) or saline, the rodent should be transferred to a small cage or box and taken to a veterinary clinic.
Self-treatment of rodents in case of injuries is not recommended, since wounds can become infected, and fractures can lead to further improper healing of bones or complete loss of a limb.
Treating constipation in a hamster at home
What to do if it becomes clear that your hamster is constipated? First of all, it is necessary to provide it with water and a small amount of succulent food, vegetables and fruits. It is better not to give hamsters laxatives. Instead, the animal is given 1–2 ml of Vaseline oil from a syringe. You need to carry out two such procedures with a difference of 20 minutes, then wait 4 hours. If the intestines have not emptied, the hamster continues to be fed with oil.
To alleviate the condition, you can inject a little vegetable oil or a mixture of baxopan with paraffin oil into the anus. This must be done very carefully so as not to damage the thin mucous membrane. Therefore, it is better to have this procedure performed by a veterinarian. After this, it would be useful to massage your pet’s tummy clockwise, and then make him move, run, and play. This activates the digestive processes.
Nasal rinsing: benefits and harms
Recently, nasal rinsing with systems such as “Dolphin”, “Aqua Maris” watering can, and rinsing according to the yoga system has become increasingly popular.
Is it really useful and safe?
Let's start with the pleasant - there really are benefits.
Firstly, when rinsing, the nasal mucosa is moistened, which in the Ural region, for example, is extremely important due to low air humidity, especially during the heating season.
Secondly, when rinsing, the nose is mechanically cleaned not only from dust particles, but also from pathogenic microorganisms (viral particles, bacteria, etc.).
Despite the obvious benefits, fans of “washing” often become patients of otolaryngologists.
The fact is that when rinsing the nose in volume, water under pressure enters not only the nose, but also the nasopharynx. It is not always possible to quickly evacuate fluid through the mouth or through the other half of the nose, especially with nasal congestion when swelling of the mucous membrane occurs. The fluid, forced to follow the path of least resistance, is sent through the auditory tube straight into the middle ear. With all the ensuing, literally and figuratively, consequences. In this case, microflora is carried into the tympanic cavity (usually the environment in the middle ear is relatively sterile). This, in turn, can provoke an infectious inflammation of the middle ear - otitis media.
In childhood, this problem becomes even more pressing. The anatomical features of young children provoke the rapid spread of the infectious process: 1. Short and gaping auditory tubes, 2. Horizontal arrangement of the auditory tubes, 3. Adenoids in the nasopharynx.
Based on the above, volumetric lavage is an extremely risky procedure, especially in young children.
To preserve the advantages of rinsing and prevent the disadvantages as much as possible, it is recommended to either spray saline solutions into the nose (sprays) or instill them.
There are two main types of saline solutions: physiological and hypertonic. They differ in the concentration of salt in the solution and, as a result, in the principle of action.
Physiological (normotonic, isotonic) solutions, 0.9% solution - correspond to the normal salinity of mucus (blood, etc.) and are used to prevent infection and moisturize the nasal mucosa.
For example, in a pharmacy you can find: “Physiomer Mild rinse” and “Moderate rinse”, saline solution, “Aqualor Soft” or “Aqualor Baby”, “Aqua Maris”, “Marimer isotonic”, “Humer 150”... Of these personally I like Physiomer and Aqualor - they have a fairly large volume of injected liquid. But the main favorite: physical. the solution (the only downside of which is ease of use) is cheap and cheerful. It can be instilled from a pipette or without pressure from a small syringe.
Hypertonic saline solutions - relieve swelling of the mucous membrane, improve the outflow from the sinuses due to the high concentration of salt in the nasal cavity. This happens due to natural physiological processes: where there is more salt, water flows there. Therefore, the fluid leaves the tissues and sinuses and enters the lumen of the nose, from where it is evacuated by simply blowing the nose.
An additional bonus is the destruction of the bacterial cell wall by the same mechanism as the removal of edema; the cells seem to “explode” from the inside. The downside is some possible drying of the mucous membrane, which goes away after stopping the drugs.
Therefore, hypertonic solutions are not recommended for use longer than 30 days. Hypertonic solutions are used, for example, for acute respiratory infections.
Here are some examples of hypertonic solutions: “Aqualor Forte”, “Humer Hypertonic”, “Aqua Maris Strong”, Quicks, “Marimer Hypertonic”, “Physiomer Hypertonic”... or 1 teaspoon of salt (either sea salt or food grade) without a slide for 1 glass of water.
Attention! For some of these drugs, the instructions do not correspond to reality. The solutions are either sprayed (head straight) or instilled.
There are contraindications. Before use, consult a specialist.
Treatment of constipation in a hamster in a veterinary clinic
If your hamster's stool does not return to normal within 24 hours after starting treatment, you need to go to the veterinarian. The doctor performs an ultrasound and prescribes treatment. To cleanse the animal's intestines, he gives an enema using painkillers. In case of intoxication and dehydration, the doctor injects the hamster subcutaneously with Ringer-Locke solution. To normalize the intestinal microflora, the veterinarian recommends a special probiotic. After a few days of examination, the hamster should recover. But if intestinal obstruction occurs, surgical intervention and rehabilitation are necessary.
After treatment, the animal is fed for some time with semi-liquid plant food: boiled buckwheat, carrots, prunes, oat leaves, parsley, dill. You can add some sunflower seeds. Dairy products, meat, eggs, flour products and dry food should not be given.
Common rodent diseases
Most often you encounter rodent diseases that develop due to improper care and unbalanced feeding.
Tympany (bloating in rodents)
A dangerous disease for rodents, since the accumulation of gases in the stomach or intestines can lead to death. The first symptom is an enlarged, firm and distended abdomen. You need to urgently consult a ratologist! To slow down gas formation, you can give your pet Espumisan or Sub Simplex to drink. Eliminate legumes, easily fermentable food, grapes, and bananas from your diet.
Diarrhea (diarrhea) in rodents
Short-term diarrhea in a rodent, combined with a healthy appearance, may indicate a non-infectious etiology of the disease. In this case, a slight nutritional adjustment will be required. Include high-quality hay in the diet, as well as high-fiber pelleted feed. It is also important to provide access to fresh water.
Constipation in rodents
Constipation in rodents is the absence of feces or a decrease in the amount of feces. The cause of the disease can be stress, pain, spoiled food, or a basic lack of water. The animal refuses to eat, becomes lethargic, and chatters its teeth. The stool becomes small, dry, or completely absent. In simple cases, it is enough to introduce more hay and fresh water into the rodent’s diet. In severe cases, such as gastrointestinal stasis in rabbits, drug therapy under the supervision of a veterinarian is recommended.
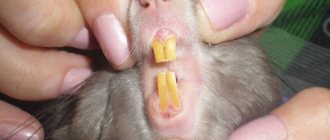
Overgrowth of incisors and cheek teeth in herbivores
This disease is characteristic mainly of herbivorous rodents. As a rule, guinea pigs, chinchillas, and degus often experience dental problems.
The development of malocclusion can be caused by a predominance of soft foods in the diet and a lack of coarse fiber. The rodent becomes picky about food, later refuses it, and loses weight. There is increased salivation and discharge from the eyes. Sometimes after eating, irregular bowel movements are observed. You need to see a veterinarian for dental treatment. Before this, you can force-feed the rodent - ground food. After grinding down the teeth, the veterinarian recommends introducing branches of fruit trees and hay into food.
Hamsters and rats are also characterized by lengthening of the incisors, associated with the lack of solid food and objects for grinding teeth. Overgrown teeth cause discomfort to the rodent and can injure its lips and soft tissues. Constantly adding wooden blocks to the cage and correcting the diet will help avoid this problem. These same representatives of the order of rodents have caries of cheek teeth. If your hamster or rat shows signs of pain when chewing food. If you are drooling or your cheek is swollen, you should immediately contact your veterinarian.
Prevention of infection
In children, worm prevention is carried out to reduce the risk of infection after contact with sick animals or people.
Basic measures to protect against infections include:
- washing hands with soap and water after visiting the toilet, public places, transport, contact with animals and outdoor games;
- pharmacological prevention of taking small doses of medications if a family member is infected;
- compliance with hygiene rules;
- proper heat treatment of fresh meat products and fish;
- boiling drinking water;
- exclusion of swimming in open waters;
- early diagnosis and treatment of infestations in domestic animals;
- sanitization of premises from flies, mosquitoes and other blood-sucking insects.
Infecting a child with parasites can negatively affect his health and delay the child's development. To reduce the risk of infection, you need to follow preventive and hygiene measures. When treating parasites, medications are needed, which are prescribed by the doctor after examining the child and receiving test results.
Symptoms of parasites in children
One of the main symptoms of worms in children is appetite.
The child eats poorly or, on the contrary, eats a lot, and at the same time remains thin. This kind of rapid weight loss happens often. This is due to the fact that parasites eat all the useful substances and nutrients, and therefore the body experiences vitamin deficiency. Infected children who lead a sedentary lifestyle are boring and capricious, because the worms feed on carbohydrates, which give energy and vigor. Another symptom is dysfunction of the digestive tract. Children are bothered by constipation or diarrhea, goiter and colitis develop. Nausea, vomiting and a feeling of heaviness in the navel or liver occur. In the course of their activity, parasites release toxic substances that lead to intoxication of the body. This threatens the appearance of nervousness, increased excitability, headaches, and body temperature can rise to 37.5°.
A sign of the presence of parasites in a child’s body is insomnia and teeth grinding during the night’s rest. Due to chronic fatigue, children may lag behind their peers in development; acute respiratory infections, flu, sore throat, stomatitis, and sinusitis become more frequent. When infected with parasites, the skin becomes dull, and allergic reactions often occur in the form of dermatitis and eczema, which are difficult to treat. A dry cough, rhinitis, and bronchial asthma may appear. Hair and nails deteriorate.
If a one-year-old child has worms, their symptoms can only be detected in the stool. At the stage of parasite reproduction, round parasite larvae or the worm itself are found in the feces. The eggs are accompanied by itching of the skin around the anus.
Manifestations of various types of parasites
There are a large number of parasites that feed on the human body. Each of them affects different internal organs and has individual symptoms.
- Enterobiasis is caused by pinworms. A characteristic symptom of the disease is severe itching of the skin in the anal area, which intensifies at night.
- Ascariasis can cause fever, dry cough and allergic reactions. When infected, the child loses weight. At an advanced stage, jaundice, pancreatitis and intestinal obstruction may develop.
- Trichuriasis causes anemia and goiter. The stool is loose, the child is lethargic.
- Urogenital schistosomiasis leads to inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs and urinary disorders.
- Trichinosis is characterized by muscle pain, chills and facial swelling in a child.
- Symptoms of opistrochiasis are liver damage, the appearance of jaundice of the skin, mucous membranes, sclera of the eyes, diseases of the pancreas, gall bladder and spleen.
The severity of the disease depends on the number of parasites feeding. If there is only one worm in the intestine, the symptoms may be almost unnoticeable; if there is a large accumulation of parasites, all the symptoms manifest themselves especially strongly.