IMPORTANT!!! A specialist must diagnose the pathology, identify the cause and treat the rat! If a domestic rat is sick, it is advisable for the owner to urgently contact a veterinary clinic; some diseases of rats are very dangerous for humans: mycoplasmosis, rabies, tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, tularemia, toxocariasis, rickettsiosis, leptospirosis, hemorrhagic fever, typhus, plague, sodoku, listeriosis.
How to tell if a rat is sick
Diseases of domestic rats often arise due to violations of feeding and maintenance standards; hypothermia, overheating or drafts cause colds and inflammatory diseases in smart animals; unbalanced diet and abuse of harmful treats cause obesity, allergies, vitamin deficiencies or intestinal pathologies in pets.
Infectious diseases of rats are also common; domestic rodents can become infected with viral, fungal and parasitic diseases through care items, food or through contact with infected relatives.
Owners of furry rodents often wonder whether a rat can get a virus or a cold from a person. Decorative rats are bred in laboratory conditions, have reduced immunity and are susceptible to human respiratory viral infections. During the acute period of the disease, the owner needs to limit communication with pets, cancel walks and games, leaving only feeding and changing water for the animal.
Diseases of domestic rats can be caused by various causes and pathogens, as a result of which a different clinical picture will be observed. The owner can understand that a pet rat is sick if his beloved rodent exhibits characteristic symptoms common to many pathologies:
- change in appetite or complete refusal of food;
- lethargy, excessive sleepiness, reluctance to play with the owner or other rats;
- changes in the color and odor of urine and feces;
- dirty genitals, the pet stops licking itself;
- dull and tousled coat, formation of bald areas;
- the appearance of causeless aggression, anxiety, nervousness;
- slowness, difficulty moving;
- breathing problems;
- unnatural poses;
- the formation of growths, bumps, swellings on the animal’s body;
- discharge from the nose, eyes, vagina, anus.
Actions after the death of a pet
Often, after the death of a beloved rat, owners do not know what to do next. How to survive the passing of your beloved pet, and what to do with the body.
Where to bury
Loving rat owners admit they can't just take a dead animal and throw it in the trash. After all, even in a short period of life, fluffies manage to become real family members. In case of loss of a pet, it is recommended to do the following:
- Arrange a funeral in a specialized cemetery intended for burying pets. Burial areas may be managed by private organizations or municipal authorities.
- If your locality does not have a designated place for burying animals, you can bury your deceased pet outside the city. To do this, you need to put the rat in a box and take it to a remote forest belt. After that, dig a hole 1-1.5 m deep and bury the box with the rat.
- Contact the veterinary clinic for cremation of the animal. Most medical institutions are ready to provide this service for a nominal fee.
Often, owners of private houses prefer to bury deceased pets right in the yard. However, this is not the best solution. Firstly, the body of the buried animal will actively produce cadaveric poison. Harmful substances will not only get into the air, but also into the soil on which fruits and vegetables will subsequently be grown. Secondly, it will be unbearable for loving owners to see the burial site every day. Especially if there are children living in the house.
How to cope with loss
For many people, pets are considered family members. Therefore, their departure causes many sad emotions - sadness, melancholy, the inability to believe what happened. Fortunately, there are several effective methods that will help you quickly cope with the bitterness of loss:
- At first, it is necessary to discuss the tragic event with family members and loved ones as often as possible. Constantly talking through the problem will help you let go of the situation faster.
- Don't try to erase your pet from your memory. To relieve the heaviness from your soul, you should, on the contrary, more often remember your favorite rat - its achievements, funny moments with its participation, the process of getting to know each other, taming, and the emergence of mutual affection. This will help you understand that the fluffy one lived a short, but eventful and happy life.
- It is necessary to put aside the feeling of guilt. Death is a natural process and is inevitable for every living being. No one can influence the coming of death. The main thing is that the owner was able to provide his pet with a comfortable and happy life.
Memorabilia or events can help you cope with the death of a rat. For example, after an animal passes away, you can edit a video about it or plant a tree in the garden. Thus, a piece of the animal will always be close to the owners.
How to understand that a rat is dying, what to do and how to help the animal are questions that interest many rodent owners. It is not always possible to sense or predict the death of an animal. Therefore, first of all, you need to make sure that the fluffy feels comfortable and safe during his life, and also do not forget to give him love and care.
Diseases of decorative rats and their treatment
Diseases in rats can be divided into two large groups, within which several subgroups are distinguished.
Contagious diseases
They are caused by various biological pathogens (pathogenic microflora, viruses, fungi) and are divided into:
- Infectious diseases of rats;
The causative agents are bacteria, viruses, fungi, rickettsia: listeriosis, ectromelia, salmonellosis, pasteurellosis, infectious pneumonia, tularemia, rabies, tuberculosis, encephalomyelitis.
- Invasive (parasitic diseases).
Caused by infection of the domestic rat's body with ticks, insects, helminths and protozoa: syphaciosis, aspiculuriosis, rodentolepiasis, hymenolepiasis, coccidiosis, demodicosis, pediculosis, fleas, scabies.
Non-communicable diseases
Decorative rats develop as a result of violation of the conditions of feeding and keeping the animal and are divided into:
- Internal;
Diseases of internal organs, blood and metabolic disorders: gastritis, enterocolitis, rhinitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, vitamin deficiencies, oncology, allergies, anemia, cardiovascular failure, ischemia, porphyrin.
- External;
Diseases of the limbs, head, neck, skin, tail - wounds, pododermatitis, injuries, skin abscesses, burns, bruises, frostbite, eczema, diseases of the eyes, ears and teeth.
- Diseases of the genital area.
Endometritis, vaginitis, pyometra, miscarriage, spirochetosis.
Treatment of pathologies of ornamental rats is carried out by a veterinarian after determining the diagnosis and determining the cause of the disease; many diseases require specific therapy or euthanasia of the infected animal.
Tips and tricks for injuries
Even the most responsible and attentive owner is sometimes unable to keep track of the animal. If a rat has torn off its skin or your pet has fallen from a height, you should remember simple rules:
- Examine your pet carefully. If the skin is severely damaged or the animal has difficulty moving, you should immediately consult a doctor.
- Find out whether the animal could have been accidentally stepped on to rule out injuries to the spine and limbs.
- Do not forget that minor tissue damage is only visible on an x-ray.
If a rat breaks its leg after falling from a great height, carefully restrain the animal and apply a splint to prevent displacement. In case of fractures, it is important to ensure complete rest and limit movement as much as possible.
When an animal's limbs are broken, the recovery process largely depends on the prompt actions of the doctor and breeder. After being examined by a veterinarian and prescribing treatment procedures, strictly follow the recommendations and make sure that the rodent does not fall again or damage the skin.
Contagious diseases of domestic rats
Infectious diseases often found in decorative rats include: mycoplasmosis, listeriosis, tuberculosis, infectious pneumonia, parasitic diseases.
Infectious diseases of rats
Domestic rodents often become infected with infectious diseases; sources of pathogens can be contaminated food, water, litter, insects, or sick animals. These pathologies are characterized by a severe course with serious damage to the vital organs of the animal, often leading to the death of the pet. Many infectious diseases of rodents are dangerous to humans; self-treatment of rats is unacceptable and can lead to dire consequences. A timely visit to a specialist can save the life of a small animal and protect the animal owner’s family from infection.
Mycoplasmosis
Most decorative rats are carriers of the causative agent of mycoplasmosis, but infection and the development of characteristic pathological changes are observed only as a result of contact with a sick animal, in violation of feeding and maintenance conditions, hypovitaminosis and weakened immunity, in elderly individuals. Pathogenic microorganisms infect the upper and lower parts of the rodent's lungs, forming numerous abscesses and causing the development of pneumonia, sometimes the inflammatory process affects the animal's genitals.
Symptoms characteristic of rats: sneezing, red discharge from the nose and eyes (porphyrin), wheezing and whistling when breathing, blue discoloration of the mucous membranes and skin, the rat has become lethargic and lies down a lot. Treatment includes a course of antibiotics, hormones, vitamins and anti-inflammatory drugs; in advanced cases, it is impossible to save a furry rodent.
Rabies
Rabies in ornamental rats is quite rare, it is very dangerous for humans, a pet becomes infected through saliva when bitten by a sick animal, especially while walking on the street, the most severe course of the disease is observed when bitten on the head or area of the nerve nodes.
The disease can occur in violent, paralytic and abortive forms; the incubation period in bitten people and decorative rats ranges from 2 weeks to three months.
Signs of rabies in rats develop gradually, in several stages:
- the first stage - apathy and photophobia are observed, followed by aggressiveness, sudden jumps around the cage, and characteristic attempts to catch non-existent flies. The rodent refuses food, salivation, vomiting, shortness of breath appear, and the pet cannot swallow due to paralysis of the lower jaw. Similar symptoms of rabies in rats against the background of recent bites should alert the owner of the rodent; it is necessary to urgently contact a veterinary clinic;
- the second stage - rabies in rats manifests itself in increased aggression, the rodent bites people, animals, cages, profuse salivation appears, paralysis of the hind limbs and pharynx, a drooping jaw, drooping head and tail are characteristic. Outbursts of excessive aggression are followed by periods of calm. The rabies virus penetrates the brain and the rat dies within 5-10 days. If a disease is detected in a decorative rat, the animal is euthanized, and the room where the pet was kept is disinfected using ultraviolet rays and alcohol.
Infectious pneumonia
The causative agents of the disease are specific viruses; domestic rodents become infected by airborne droplets; the pathological process occurs in the upper parts of the lung of a domestic rat. The pathology is manifested by characteristic symptoms: sneezing, red and mucopurulent discharge from the nose and eyes, hunched back, wheezing and whistling, the rodent breathes heavily on its sides, refuses food, the rat is lethargic, apathetic, sleeps more than usual. Sometimes a rapid course of the disease is observed, due to the increased level of metabolism in rats; in advanced cases, the animal cannot be saved. Treatment is carried out using antibiotics, hormones, vitamins and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Papillomas in rats
The papilloma virus in rats is manifested by the formation of small skin growths on the skin, which can degenerate into malignant neoplasms. Infection occurs through contact with a sick animal through damaged areas of the skin (wounds, cracks, scratches); the disease manifests itself only in emaciated, weakened or elderly individuals. If papillomas are detected, they must be surgically removed.
Parasitic diseases of rats
Most often, decorative rats are affected by ectoparasites - parasitic insects, infection occurs through food, filler, clothing and hands of the owner, upon contact with sick animals, characteristic symptoms of the disease are severe anxiety of the animal, sores on the neck of the rat, scratching and wounds on the head and shoulders fluffy rodent. To treat a pet, treat it with insecticidal sprays.
Lice and lice
Small insects, you can find adult red-brown insects or nit eggs in the form of white dandruff attached to the rodent's fur. Lice feed on the blood of a domestic rat, lice eaters feed on skin flakes and blood; parasitism is accompanied by severe itching and can cause the death of the animal.
Fleas
Small blood-sucking insects that can migrate between rats, dogs and cats; a sick rodent itches intensely, bites fur with its teeth, and worries. If a rat has bloody crusts on its back, this indicates that the pet is infected with fleas and requires immediate treatment.
Ticks
Rat mites live on the skin of healthy animals, exhausted and weakened animals become ill, parasitism is accompanied by itching, the rat has sores on the neck and face or red-yellow growths on the ears and genitals. Some types of rat mites are dangerous to humans.
Worms
Parasites are localized in the internal organs of rats: intestines, kidneys, liver, lungs; migration of larvae causes inflammatory processes in the affected organs; worms produce poisons that cause exhaustion and intoxication of the rodent. The owner may notice intestinal disorders in the pet, lethargy, progressive weight loss, and detection of parasites in the feces. Treatment includes the use of deworming medications.
Skin injuries
While playing or walking around the house, it is important for owners to keep an eye on their pet to protect it from fractures and soft tissue injuries. Remember that rodent skin is very sensitive and can be damaged by awkward movements.
If a rat has skinned its tail, treat the surface with a disinfectant and visit a doctor. In some cases, the area needs to be amputated, but with proper and timely treatment, the tissue is restored.
When several animals are in the same cage, it is important for owners to monitor the behavior of their pets so that during play they do not tear off the skin or cause injury to each other. During sleep, the animal may fall, so you should ensure that there are no thorny or dangerous objects.
Active animals often receive burns and scratches on their tails and paws. If there is an open wound, it must be treated. If the area of skin that is scraped or damaged is significant, the wood litter should be replaced with a cloth to prevent infection.
Common non-contagious diseases of domestic rats
Among non-communicable diseases in domestic rodents, the following are common: cancer, dental pathologies, urolithiasis, intestinal disorders, obesity, allergies, coronary heart and brain disease, heart and kidney failure.
Tumors
Oncological diseases often affect adult ornamental rats over two years of age, mainly females, and cause the death of their beloved pet.
Benign neoplasms are subject to surgical removal with a favorable prognosis; rat cancer is not treated due to the formation of metastases and the germination of malignant tumors into healthy tissues of the animal. The following types of tumors are often found in decorative rats:
- a tumor of the mammary glands is detected as a mobile lump on the abdomen or fused with the skin;
- a tumor on the neck, on the side, under the paw or under the tail feels like a rolling ball under the skin on a leg;
- the swelling on the face looks like a pet's swollen cheek;
- brain tumor (BTU) is a common benign tumor with a characteristic clinical picture: the rat’s front and hind legs have failed, the rodent lies with outstretched limbs, the joints cannot be bent;
- bone tumors are manifested by thickening of the bones of the limbs, ribs and skull, the animal is not able to move independently.
Allergy
Allergies in rats occur quite often to the action of external irritants, which can be litter, food and water. Allergies in domestic rats are accompanied by itching and manifested by characteristic symptoms: active scratching of the skin, the appearance of wounds and scabs on the paws and neck, swelling of the limbs and skin behind the ears. Signs of allergies in rodents are similar to symptoms of insect parasitism; diagnosis of the disease and examination of the animal should be carried out by a veterinarian. Treatment of allergies in rats involves the use of antihistamines, anti-inflammatory ointments and eliminating the source of the allergen: changing the filler and feed.
Rhinitis
Rhinitis in rats occurs through contact with infected animals or people (infectious rhinitis) or when the conditions of detention are violated (non-infectious rhinitis). Symptoms of infectious rhinitis in rats develop rapidly, the disease is transmitted by airborne droplets, and in weakened, emaciated and elderly animals, the pathology can be fatal. If a rat has a cold, non-contagious rhinitis occurs.
Infectious runny nose in a rat is manifested by mucopurulent discharge from the nose, sneezing, grunting, red discharge from the nose and eyes, lethargy, increased general body temperature of the animal, shortness of breath, heavy breathing and wheezing. Rhinitis should be treated by a veterinarian using antibacterial, hormonal and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Colds in rats occur when the animal is in a draft, hypothermia, or sudden changes in temperature in the room; contributing factors are insufficient feeding and unsanitary conditions for keeping the rodent. If a decorative rat has a cold, the runny nose will be mucous, there is grunting, sneezing, and the animal rubs its nose with its paws. Treatment of a runny nose must begin at the first symptoms of the disease; sick pets are prescribed inhalations and antibacterial drugs; non-contagious rhinitis can cause pneumonia in a domestic rat.
Diarrhea
Diarrhea in a rat occurs as a result of violation of the conditions of keeping and feeding the pet, against a background of stress, and diarrhea can also be caused by the development of an inflammatory process in the animal’s intestines due to infectious and parasitic diseases. The disease manifests itself in the frequent discharge of light, watery feces with an unpleasant odor; mucus and streaks of blood may be present in the feces.
The owner of a rat needs to know what to do if a rat has diarrhea in order to prevent dehydration and exhaustion of the animal. If your animal has soft stool with mucus, you can give your pet rice water and diluted smecta 3 times a day for three days, and also exclude prohibited foods. If there is no improvement, or the animal’s diarrhea initially occurs with the release of a large amount of liquid foamy mass with blood and mucus, it is necessary to urgently contact a specialist.
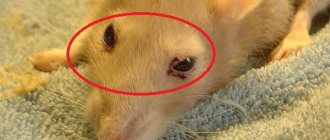
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane of the eye caused by microtrauma or viral infection. The disease is manifested by purulent discharge from the lacrimal canal, the animal's eyes, and dried crusts of pus are found on the eyelids. If a rodent's eye is inflamed, it is necessary to urgently take the pet to a specialist; the animal needs to wash the conjunctival sac with antiseptic solutions and place hormonal and anti-inflammatory ointments under the eyelid.
Corns (pododermatitis in rats)
Pododermatitis in elderly or overly well-fed rats occurs when animals are kept on hard, dry litter or in cages with slatted floors; the dry skin of the feet is damaged and rounded calluses are formed in rats, reminiscent of human calluses. Subsequently, periodic opening and suppuration of these swellings occurs, lameness and chronic irreversible processes occur in the ligamentous apparatus of the pet’s limbs. Treatment of pododermatitis must begin immediately when the feet become red; therapy consists of moisturizing the skin with oils and creams, and the corns are lubricated with wound-healing ointments. An important preventative step is changing the conditions of keeping and feeding.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis in rats is an inflammatory disease of the supporting-retaining apparatus of the tooth, manifested by refusal of food, bad breath, redness and bleeding of the gums, yellowing of the teeth, excessive salivation, sometimes with blood, loosening and loss of teeth, swelling of the muzzle. The disease develops when the rules of feeding and maintenance are violated, or an unbalanced diet using predominantly soft feed. If a rat's teeth have turned yellow, it is necessary to urgently review the diet; solid food removes tartar well, preventing the development of periodontitis. Treatment of the disease in advanced cases includes removal of diseased teeth and tissues under local anesthesia.
Porphyrin
Porphyrin in decorative rats manifests itself as burgundy-red secretions of the Harderian gland from the nose and eyes, resembling dried blood in appearance. Porphyrin occurs independently due to injuries, stress, violation of feeding and maintenance conditions, or signals serious pathological conditions in the body: pneumonia, mycoplasmosis, oncology, tuberculosis. Treatment of porphyrin comes down to improving feeding conditions, housing, eliminating stress and symptomatic therapy.
Stroke
Stroke is a common pathology in decorative rats, characterized by impaired cerebral circulation as a result of rupture or blockage of blood vessels in the brain. Individuals suffering from obesity, heart and kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, and oncology are predisposed to the disease. A stroke manifests itself as loss of coordination, paralysis of the limbs, blindness, breathing problems, eye hemorrhages, the rat walks sideways, and the rodent may become apathetic or aggressive. Treatment is effective in the first hours after the onset of the disease; the animal is prescribed oxygen, diuretics and antiepileptic drugs.
Abscess
An abscess is a focal inflammation of tissue, a fairly common pathology in domestic rats, which occurs when the integrity of the skin is damaged against the background of reduced immunity. An abscess is characterized by the formation of a swelling filled with pus. Treatment of the disease is carried out only by a veterinarian using surgical dissection using local anesthesia. Treatment at home can cause infection of healthy tissue, sepsis and death of the pet.
Our advantages
A rat fell from a height in Rostov-on-Don - we have the solution.
That's why they choose us to bake.
Pet taxi
We will help your friend at home, or transport him to the clinic, using our own zoo-taxi
Seven days a week
Our only day off is January 1st. You can contact us any day, we work around the clock, without days off or breaks.
New technologies
The clinic’s equipment makes it possible to perform operations that are inaccessible to other veterinary hospitals in the city.
Good plus
You can purchase medicines and food for your animal directly from our clinic.
Let's be professional
Our doctors are professionals with extensive experience and a responsible approach to their work.
Let's improve
We are members of the Union of Pet Business Enterprises of Russia, initiators of programs for the development of progressive veterinary medicine and animal care.
Chemical substances
There are 90 billion nerve cells in our brain; they come into contact with processes, forming contacts - synapses. At synapses, signals are transmitted by neurotransmitters. These substances, called neurotransmitters, are important for understanding how the brain works.
And these same substances are the basis of psychopharmacology. With the help of them we try to control or correct the functioning of the brain
The main mediators of the central nervous system:
Glutamate
- stimulating, transmits the main information flows in the brain, is associated with sensory, memory, and preparation of movements.
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
- inhibitory, blocks information flows, provides motor control, emotional control, sensory control (when we can listen to one voice and not turn to another).
Because GABA is the main inhibitor; its role in falling asleep is great. If we shift the balance towards more GABA, we fall asleep more easily.
More often the opposite problem occurs when the concentration of glutamate is higher. In adults it is nervousness and insomnia; in children it sometimes looks like ADHD.
The most serious excitation-inhibition imbalance is epilepsy.
To shift the balance in favor of inhibition, drugs that activate GABA synapses are used.
Classic sleeping pills - barbiturates, benzodiazepines.
Phenobarbital is one of the well-known and over-the-counter molecules that is part of Corvalol, Valocordin.
Valerian has a similar, but weak effect.
Sometimes they use pure GABA in tablets, but it hardly passes into the brain, and if it does, it does not work as an inhibitory neurotransmitter, but rather as food for nerve cells. So it's more of a nootropic than a sedative.
Serotonin is also important for triggering a sleepy state. Poor functioning of the serotonin system is a prerequisite for depression and insomnia.
You can help a little with drugs containing the molecule from which serotonin is made. Again, this is the level of dietary supplements and nootropics.
Our body produces glutamate and GABA easily and in any quantity.
To make serotonin, you need a tryptophan molecule. We get tryptophan from food proteins and cannot make it ourselves. Taking it in tablet form can have a mild dietary supplement effect and improve sleep. Manufacturers’ positioning of tryptophan-containing drugs as antidepressants is clearly overkill.
The specificity of dietary supplements is that they do not help everyone, but if they help, they allow you to gently correct some problem.
Tryptophan in our nerve cells is converted into 5-hydroxytryptophan, and then into serotonin. 5-hydroxytryptophan is also offered as a supplement. It works a little more reliably, but still remains a dietary supplement.
A mediator with the opposite effect, i.e. interfering with sleep is called norepinephrine.
A computer game, a parachute jump, or a sports victory are norepinephrine types of pleasure.
Molecules similar to norepinephrine also interfere with sleep. For example, some cheese components. Norepinephrine is formed from the amino acid tyrosine. And the bacteria that make cheese can convert tyrosine into tyramine. And tyramine is similar to norepinephrine.
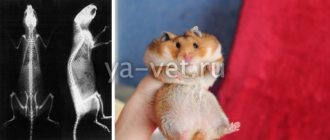
Determining the sex of baby rats
The most difficult thing is to determine the sex of a newborn rat. Immediately after birth, differences in anatomy are not noticeable, since the genitals are not yet formed. But you can do it if you know what to look for.
Newborn rat pups are born without fur and are approximately the same size. Therefore, trying to determine gender by indirect signs is useless. In this case, you should pay attention to the baby’s tummy, as well as private parts.
You should try to determine the sex of babies no earlier than the 5th day after birth. The girl rat has small nipples on her stomach, which are located in 2 rows. They are just beginning to form, so they look like small pimples. The little rat has no such formations, his tummy is simply smooth.
Also, when identifying sex in newborns, you need to consider the area where the genitals are located. Small dark spots can be seen in the space between the urethra and the anus. These are the future testicles of the male, which are just beginning to form. Females do not have such spots.
Melatonin
Melatonin is controlled by the hypothalamus. The release of melatonin is inhibited by visual signals. Even through the eyelids, bright light prevents the pineal gland (the piece of the brain where the black cursor is pointing in the picture) from releasing melatonin.
If your regime is biased towards sleeping during daylight hours, then take care of thick curtains.
Melatonin disperses throughout the body and reduces the activity of all systems: the heart beats slower, intestinal function slows down, and body temperature drops. Plus it is an important antioxidant.
For sleep problems, it is recommended to take melatonin tablets. This substance also has a mild effect, at the level of a dietary supplement. If you often change time zones, understand the importance of melatonin. As you age, problems with melatonin production may arise.
Nervous system
The brain stem, ancient, evolutionarily early emerging zones. They are responsible for breathing, controlling heart rate, etc. Sleep and wakefulness are for the most part also associated with these structures.
The brain stem includes:
- Medulla
- Bridge
- Midbrain
- Diencephalon (between the hemispheres)
What is marked with yellow circles on the diagram is the most important centers of sleep and wakefulness.
This is if we talk about the macro level. And at the micro level, our brain is cells, and their functioning is highly dependent on the state of the sleep and wakefulness centers. This is something like a power supply.
A person has needs, among them Academician P.V. Simonov identified vital needs (vital):
- food (energy, building materials)
- drinking (water-salt metabolism)
- safe (passive and active defensive)
- homeostatic (respiration, blood circulation, thermoregulation, sleep, wakefulness)
- saving energy (“laziness reflexes”)
- grooming (“body care”)
Homeostasis is the constancy of the internal environment of the body.
Pressure, the amount of oxygen and microelements, all this is included there. And to maintain homeostasis, you need to sleep. Prolonged sleep deprivation causes disruption of homeostasis and stress, and can be fatal.
Sleep, first of all, equals rest. But that's not all. The ancient Greeks understood this. In their pantheon there were 2 gods of sleep - Hypnos and his son Morpheus. The first is the god of sleep, the second is the god of dreams. The Greeks understood that sleep can be rest, or it can be a state in which something chaotic happens, there are “prophetic” or creative dreams. And there are nightmares and “pseudo-prophetic” dreams. The Olympians sometimes used Morpheus to intimidate some hero so that he would not go where he shouldn’t.
We will talk about both the state of sleep and the state of dreams. But let's start with something simple.
When is the right time to wake up?
At the end of the second column.
When brain activity is almost awake. If you go into the green phase, especially where the greenest bars are, it is very difficult to wake up a person, and it will be long and difficult for him to wake up, because... the brain is in a very “slow” state. How do devices that promise to wake you up at the right time work?
The most accurate are rag pads with eye movement sensors. As soon as you stop actively moving your eyes, it’s time to wake you up.
Dreams are often emotions. Emotions quicken your pulse. Smart watches will be able to correctly wake you up based on your pulse.
During the REM sleep phase, a person does not move. When a sleeping person was sleeping and sleeping, and suddenly began to stir, you can wake him up. This is done by devices that simply listen to you sleep. But there is no accuracy here.
Our main center of wakefulness is located inside the bridge. There are cells there that collect signals from all sensory systems. Any of our sensory systems can influence our state of wakefulness: the alarm clock rings, the light shines in our eyes, they gave us ammonia to sniff, we shook our shoulder.
Nerve cells of the reticular nuclei of the pons (upper right corner of the picture above, A-block). When they were discovered and described in the 20th century, they could not understand what kind of cells they were and why they reacted to everything. And this turned out to be the main center of wakefulness.
Key sleep signals travel to the midbrain. Midbrain neurons produce serotonin (5-HT). NREM sleep is influenced, among other things, by serotonin. We maintain a little muscle tone.
When we enter REM sleep, the locus coeruleus, which is located inside the pons, releases the molecule norepinephrine as a neurotransmitter. Norepinephrine blocks serotonin, blocks muscle tone, but allows the cortex to move into a more active state.
The fact that norepinephrine blocks muscle activity is very important. If you don’t block the muscles, dreams provoke a reaction, your arms and legs will run and grab. It happens, but it is pathological.
By the way, sleepwalking or somnambulism is associated with slow-wave sleep. Residual brain activity causes the person to move slowly and can be put back down.
But fighting during sleep is a violation of the paradoxical sleep phase.
More about drugs
Glycine - passes into the brain very poorly, affects the level of dietary supplements, but for some it has a slightly calming effect.
Histamine is a substance that is associated with inflammation. Antihistamines are what you take when you have allergies. Antihistamines have a side effect - a inhibitory effect on the brain. The creative thought of pharmacologists turned a side effect into a main one. These include anti-motion sickness pills and tranquilizers to relieve anxiety and improve sleep.
Caffeine has an activating effect. When the body gets tired, the adenosine molecule is produced in large quantities. Caffeine prevents adenosine from transmitting the signal of fatigue, resulting in an invigorating effect. Because This is not additional energy, but lending from one’s own resources.
Domestic decorative rats: gender differences in appearance
Male and female house rats are equally cute and fluffy, but differ slightly in appearance. The main indicators are size, body shape and coat properties. Gender differences in appearance are described below.
Male rats by :
- Larger size and weight
- Quite hard, dense wool
- Pear-shaped body structure
The distinctive features of a girl rat are:
- Smaller body size compared to males
- Elongated torso
- Silky, smooth and shiny fur
In addition to appearance, an important criterion for owners is the smell. Males smell stronger, mainly due to their habit of marking territory. However, with good care you can reduce it to a minimum.
Preventive measures
It is advisable to engage in extermination of rats before repairs . This can be done in a variety of ways:
- Glue-based traps with bait in the middle: they are installed not far from the hole, so that later they, along with the stuck victim, can be easily removed;
- Mechanical rat traps: installed along the route of the rodent;
- Repellent odors;
- Ultrasonic rat repellers.
One of the popular fishing methods is Victor electric rat traps with ready-made baits. In appearance, the trap is a two-story container: the rat runs into it, goes to the second floor with the bait, is subjected to a strong electrical discharge and, killed, falls into a special compartment on the first floor.
Repelling mice and rats using ultrasound (for example, the Tornado-200 or Tornado-300 device) is one of the most promising methods of deratization.
It is worth remembering that the ultrasonic signal of the trap does not pass through hard surfaces, in addition, the pile of carpets can hide its effect.
At the same time, in order not to resort to using the device every time the rats return to the home, it is necessary to worsen their living conditions as much as possible: install protective metal mesh, seal the holes.
Paradoxical dream
We spend approximately 20% of our sleep time in the REM sleep stage.
If a person is woken up at this stage, he will most likely say that he had a dream. But he most likely will not remember dreams at other stages. In the final stages of paradoxical sleep, dreams are usually light. Nightmares are more common in the early stages, and they can be so overwhelming that they jolt you out of sleep. About one in 15 people have dreams every day.
Creative people value their dreams very much. On the slide are sketches of the dreams of Salvador Dali and Marc Chagall:
Back in the 19th century, Sechenov said that dreams are unprecedented combinations of experienced impressions.
First of all, the brain deals with the information of the day; the structure of the hippocampus helps it with this. And then you can deal with something that has been accumulated almost throughout your life.
If you clearly set a task for the paradoxical sleep system before going to bed, then it is able to continue solving this problem in a dream, and you will find a solution. Or you will wake up with a ready-made solution.
Anecdote on the topic:
At first, Pushkin dreamed of the periodic table, but he did not understand anything.
In order for information to be recorded in long-term memory, you need to sleep correctly and allow the paradoxical sleep phase to work with the received data.
First, the information of the current day is “written” to a structure called the hippocampus. And only then is it rewritten throughout the cerebral cortex. Essentially, the hippocampus is operative memory, and the cerebral cortex is long-term memory. And rewriting, apparently, occurs during paradoxical sleep.
Also I.P. Pavlov understood that for effective learning the brain needs the right state:
As you can see, in addition to the state of the brain, it is important that the information is also meaningful to you. Otherwise, the antispam system will work, which does not need anything extra.
By the way, the “edge effect” works well. We remember better information that was received at the beginning of the day and just before bed.
This is what our hippocampus looks like from different angles:
Translated from English, hippocampus means “seahorse”. Neuroanatomists were apparently poetic people.
The hippocampus contains neural networks that are capable of capturing some information almost instantly. For example, in the next 10-15 minutes you will definitely remember the word “hippocampus”.
The hippocampus has interesting properties:
A small memory capacity, for example, does not allow us to perceive the first 10 minutes of a lecture and the end of the second hour of a lecture equally well.
New information is stored during the “working day”, and rewriting partly depends on the emotional background. Sometimes we memorize information that we would like to forget and cannot remember the necessary information. But this is a slightly different topic.
During rewriting, processes of generalization and association with other fragments of your experience take place. The more interesting your day was, the more REM sleep you will have that night.
On average, children have longer REM sleep than adults, apparently because... the world is new to them.