Diagnostics
| SERVICE | PRICE |
| Initial appointment | 500 rub. |
| Repeated appointment | 200 rub. |
| Urgent departure | from 500 rub. |
| Ultrasound | 1500 rub. |
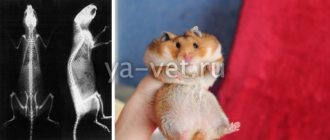
| X-ray | 1000 rub. |
| Analyzes | from 800 rub. |
| Gastroscopy | 6000 rub. |
| ECG | 1500 rub. |
| Microscopy | 800 rub. |
| Laboratory research | from 800 rub. |
Surgery
| SERVICE | PRICE |
| Castration | from 1500 rub. |
| Sterilization | from 2500 rub. |
| Laparoscopy | from 4500 rub. |
| Obstetrics | from 3000 rub. |
| C-section | from 4000 rub. |
| Fractures (plaster application, osteosynthesis) | from 2000 rub. |
| Tumor on the skin (removal) | from 1000 rub. |
| Tumor on the mammary glands (removal) | from 1000 rub. |
| Trimming hooks, incisors, teeth | from 300 rub. |
| Tooth extraction | from 500 rub. |
| Removing foreign objects from the stomach | from 6000 rub. |
| Removal of claws and fingers | from 500 rub. |
| Hernia removal | from 2000 rub. |
| Pyometra removal | from 3000 rub. |
| Removal and treatment of the 3rd eyelid | from 3000 rub. |
| Suturing wounds | from 1000 rub. |
| Opening abscesses | from 1000 rub. |
| Postmortem autopsy | from 3000 rub. |
| Treatment and treatment of wounds | from 500 rub. |
| Anal glands, inflammation and treatment | from 500 rub. |
Therapy
| SERVICE | PRICE |
| Injections | from 200 rub. |
| Droppers | from 500 rub. |
| ICD (urolithiasis) | 2500 rub. |
| Genitourinary system | 2500 rub. |
| Urinary incontinence (cystitis) | 2500 rub. |
| Gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract) | 2500 rub. |
| Treatment of skin diseases | from 500 rub. |
| Treatment of otitis media | from 500 rub. |
Prevention
| SERVICE | PRICE |
| Vaccination of pet rats | from 1000 rub. |
| Treating beds and rooms against parasites | from 500 rub. |
| Treatment for worms (anthelmintic) | from 300 rub. |
| Selection of food for a decorative rat | from 500 rub. |
Funeral services
| SERVICE | PRICE |
| Euthanasia | 1000 rub. |
| Humane euthanasia | from 1000 rub. |
| Cremation | 1000 rub. |
| Cremation with return of the urn with ashes | from 3000 rub. |
| Establishing the cause of death | from 3000 rub. |
Consultation with specialists
| SERVICE | PRICE |
| Therapist | 500 rub. |
| Dentist | 500 rub. |
| Ophthalmologist | 500 rub. |
| Surgeon | 500 rub. |
| Oncologist | 500 rub. |
| Dermatologist | 500 rub. |
| Traumatologist | 500 rub. |
| Orthopedist | 500 rub. |
| Ratologist | 500 rub. |
| Psychologist | 500 rub. |
Additional services
| SERVICE | PRICE |
| Sanitary haircut (grooming) | from 1500 rub. |
| Consultation on care and maintenance | from 500 rub. |
| Support after operations. Overexposure | from 1500 rub. |
| Hospital | from 1000 rub. |
| Taxi | from 1000 rub. |
Get a free consultation>>>
All animals, not excluding ornamental rats , can suffer from a wide variety of diseases, especially if they are kept in a cage. Being in a closed space does not have the best effect on the condition of our pets, lowering their immunity and resistance to various diseases. If your pet gets sick, a veterinarian for decorative rats will come to his aid.
They are relatively weak and sickly animals. Therefore, even if your animal appears to be completely healthy, it must be regularly brought to the veterinary clinic for routine examinations by a veterinarian. Up to one and a half years - once every six months, over one and a half years - once every 3 months. In order for your ornamental rat to live with you for as long as possible, you must adhere to a sanitary regime, proper nutrition, and at the first signs of illness, immediately contact a veterinarian.
How to understand that your pet is sick
There are several signs that, even before an accurate diagnosis is made, indicate the presence of the disease in decorative rats. The most common painful symptoms in rodents include:
- deterioration of mood, lethargy, apathy;
- weakened state, the pet prefers to sit in one place because it has difficulty moving around the cage;
- dulling of fur;
- the appearance of bald patches;
- decreased or complete lack of appetite;
- red nasal discharge – porphyrin;
- sneezing, coughing;
- drowsiness;
- unreasonable aggression, anxiety;
- change in stool;
- impaired coordination of movements.
If any of the listed signs appear, it is necessary to take the animal to the veterinary clinic as soon as possible. Delay in treatment can be fatal for the rat.
What are the most common diseases of domestic rats?
Decorative rats, like any other animals, are susceptible to many diseases. However, some pathologies are most common in small rodents. Such diseases include:
- Oncology . Rats are prone to developing tumors. Most benign tumors are removed surgically. Malignant neoplasms, unfortunately, cannot be treated.
- Colds . Decorative rats are very sensitive to the slightest changes in environmental conditions. A slight draft or a drop in temperature of a few degrees can trigger a cold.
- Infections of viral, fungal and bacterial nature . The immunity of rats is quite weak, so when encountering pathogenic microorganisms, the animal’s body offers practically no resistance.
- Parasitic diseases . Rodents are subject to invasion by both external (ticks, fleas) and internal parasites (helminths).
Many diseases of decorative rats develop against the background of improper keeping of furry rats. For the well-being of rodents, care must be taken to maintain a comfortable microclimate and cleanliness in the cage.
Diseases of the urine storage and excretion system
Most often, rats and mice suffer from chronic nephropathy, cystitis or urolithiasis.
Nephropathy
Usually occurs in older pets. The kidneys of the sick animal are enlarged. A huge amount of protein is detected in the urine.
Urolithiasis disease
Veterinarians classify urolithiasis as a pathology caused by improper feeding. Blood appears in the urine. With ICD, the urge to urinate may not result in the passage of urine. The animal becomes nervous and refuses food.
Cystitis
Cystitis can be infectious or traumatic. With these diseases, the animal sits down in a forced position, hunches, and squeaks. Urine comes out in very small portions. The animal shows nervousness.
Non-communicable diseases: symptoms and treatment
A feature of non-contagious diseases of ornamental rats is the impossibility of transmitting pathology from a sick animal to a healthy one. Such diseases most often develop against the background of genetics, due to poor living conditions, and unfavorable environmental factors.
Abscesses
Rats are very active and curious animals. During games and exploration of the surrounding space, fluffies often receive small wounds - abrasions and scratches. Also, similar damage can occur after rare fights with relatives.
Microtraumas themselves are not dangerous, but if pathogenic microorganisms get inside, the damage becomes inflamed and suppuration appears. A pus-filled lump appears inside the subcutaneous fat. It is strictly forbidden to open such abscesses at home. More details in the article “Symptoms and treatment of abscess.”
If during an abscess the contents of the capsule leak into the tissues, blood poisoning will occur. In such a situation, the disease is 100% likely to end in death.
Allergy
Most often, decorative rats experience allergic reactions to food. Pathology manifests itself in the form of itching, skin rashes, partial hair loss, and tearfulness. Potential allergens for rodents are:
- eggs;
- oranges;
- tangerines;
- grape;
- grapefruit;
- peaches;
- peanut.
However, individual intolerance to other foods cannot be ruled out. Also, allergic reactions can be caused by the filler in the cage. Pine sawdust is considered especially allergenic.
The only way to treat is to identify the irritant and eliminate it from your pet’s life forever. If you cannot identify the allergen on your own, a ratologist will help.
Neoplasms
Rats are genetically predisposed to tumor diseases. The tumor can grow in any part of the body, in any organ. The main symptom of the pathology is the appearance of a lump under the skin. The general well-being of the rodent may also deteriorate. The sooner you show the animal to the veterinarian, the better.
If the diagnosis shows that the tumor is benign, the pet will undergo surgery. The tumor will be removed under general anesthesia, after which the rat will need 7-10 days to fully recover. During this period, the animal will require special care.
If a malignant tumor is detected, the rat is not treated. Fluffy will be sent home to live out his last days. If the rodent's condition worsens significantly, the doctor will most likely suggest euthanizing the animal.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
Most often recorded in older animals with concomitant pathologies. It is quite difficult to determine heart disease externally. Changes in behavior may indicate a deterioration in the animal’s well-being:
- decreased vital activity, lack of interest in current events;
- weakness;
- drowsiness;
- coughing;
- the animal often raises its head - this position makes breathing easier.
Also, the animal’s paws noticeably swell and become cool to the touch. If these symptoms appear, you will need to contact a veterinary clinic for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Cold
Decorative rats have a fairly weak immune system, so hypothermia or the slightest draft can cause a cold. The disease is manifested by sneezing, grunting and the discharge of clear mucus from the nose.
Typically, inhalation and antibiotics are prescribed to treat colds in rodents. It is worth noting that under no circumstances should colds be left to chance, otherwise the cold will eventually develop into pneumonia.
Stroke
Hemorrhages or disturbances in the blood supply to the brain of decorative rats are most often caused by concomitant diseases: tumors, diabetes mellitus, diseases of the cardiovascular system, thrombosis. The presence of a stroke in a rodent may be indicated by the following pathological symptoms:
- weakness;
- partial or complete paralysis of the paws;
- intermittent breathing, shortness of breath;
- bleeding in the eyes;
- blurred vision;
- muscle cramps.
If you have a stroke, it is important to take your pet to the veterinarian as soon as possible. To treat the pathology, oxygen, corticosteroids, diuretics, and nootropics are usually prescribed. Also, after suffering from an illness, the fluffy needs special care.
In case of partial or complete paralysis, you will need to help your pet change body position to avoid bedsores. It is also necessary to remove all ladders, shelves, and hanging hammocks from the cage. Feeders and shelves should always be “at hand” for a sick animal.
Household problems in rats and other rodents
Domestic rodents have a number of advantages, for example, they are smart (especially rats), but at the everyday level they have plenty of problems. Among them:
- Rodents chew (forgive the tautology) almost any thing, so you need to be careful with your things;
- Your pet's cage will need to be cleaned frequently;
- Rodents are predominantly nocturnal, so their noise at night will disturb people with light sleep;
- A rodent's cage usually needs to be spacious, which is why it often takes up a lot of space. Putting it in a secluded corner will not work;
- If you get a rat, then you risk becoming an object of ridicule and teachings like “they were the reason for the plague”;
- And finally, rodents live very little even with ideal care, that is, no more than 5 years, with rare exceptions.
Infectious diseases: symptoms and treatment
A feature of infectious diseases is the possibility of transmission of pathogenic microflora from one animal to another. Therefore, sick rats must be placed in a separate cage until complete recovery. When caring for an animal sick with infectious diseases, the owner will need to especially carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Salmonellosis
The disease is caused by the pathogenic bacteria Salmonella. Infection usually occurs through dirty water or food. Most often, salmonellosis in rodents is recorded in the heat, since the activity of salmonella at high temperatures increases significantly. The presence of pathology can be determined by the following signs:
- bloating;
- liquid stools of a greenish color, with a strong unpleasant odor;
- jumps in body temperature;
- weight loss;
- weakness.
Treatment must be started as soon as possible, otherwise death cannot be avoided. The basis of therapy is the use of antibacterial drugs (Levomycetin, Cefatoxime, Kanamycin), enterosorbents (Polysorb, Smecta), B vitamins, ascorbic acid.
Mycoplasmosis
The development of pathology is provoked by bacteria of the genus Mycoplasma. Pathogenic microflora enters the body primarily through airborne droplets, but can also enter through contaminated food. Symptoms of mycoplasmosis include:
- decreased vital activity;
- lack of appetite;
- noisy rapid breathing;
- discharge of porphyrin from the nostrils and eyes;
- cyanosis of the skin and mucous membranes.
In some cases, mycoplasmosis can affect the organs of the reproductive system. In males, symptoms are difficult to notice. But in females in such situations, quite abundant purulent-bloody discharge from the vagina appears.
Mycoplasmosis is treated with antibiotics - Azithromycin, Tylosin, Chloramphenicol. In advanced stages of the disease, therapy is supplemented with bronchodilators (Fenoterol, Ephedrine) and corticosteroids (Prednisolone, Metypred). Untreated disease leads to the development of pneumonia and death of the animal.
Papillomas
The development of the disease is provoked by viral particles that are transmitted to the rat from a sick animal through microtrauma. For example, through scratches or a bite.
In its inactive form, the virus may not manifest itself in any way. But when favorable conditions occur (weakening of the animal’s immunity), viral particles are activated, and papillomas grow on the skin and mucous membranes of the rodent. The danger of growths lies not only in the inconvenience for the pet, but also in the possibility of degeneration into a malignant tumor.
Treatment consists of surgically removing the papillomas. Also, to prevent relapse, the veterinarian may prescribe vitamin-mineral complexes and immunomodulatory drugs to the rat.
Smallpox
A viral disease is transmitted from an infected animal or virus carrier to a healthy rat by airborne droplets. The risk of infection increases in the cold season, with weakened immunity, stressful situations, and poor living conditions.
The owner of a sick rodent is also at risk of infection. Smallpox can occur in two forms:
- Spicy . The pathology does not manifest itself in any way, there are no pathological symptoms. Then a sharp deterioration in the animal’s well-being occurs, and within 1-2 days the pet dies.
- Chronic . Characteristic symptoms: rashes and wounds on the tail, paws, ears. Over time, swelling increases. In severe cases, necrosis of the affected tissues is observed. The animal suffers from the listed symptoms for 2-3 months, after which it overcomes the disease or dies.
Unfortunately, there are currently no effective treatments for smallpox. Therefore, depending on the severity of the disease, the veterinarian will suggest either euthanizing the animal or giving hope for its recovery.
Decorative rats that have overcome smallpox receive lasting immunity for life. Once a pet has overcome smallpox, the disease is no longer in danger.
Parasitic diseases: symptoms and treatment
The development of parasitic diseases in rodents is caused by the activity of external or internal parasites. With timely treatment they have a favorable prognosis. Infection, as a rule, occurs through the consumption of low-quality food or improper maintenance of decorative rats.
Ticks
They stick to warm areas of the body with the most intense blood supply - ears, neck, groin area, skin folds. It is impossible to visually detect blood-sucking parasites on the body of an animal.
The only exception is that if mites have attached themselves to the ears, the edges of the ears will be lumpy and uneven. The following symptoms may indirectly indicate the presence of bloodsuckers:
- scabies;
- the appearance of wounds on the body;
- pet irritability;
- sleep problems.
A veterinarian will make an accurate diagnosis. For treatment, specialized drugs are used, for example, Stronghold drops, Dironet Spot-on, Parasiticide-complex.
Lice and lice eaters
Small insects 0.5-3 mm in size. Lice feed on the blood of warm-blooded animals. The food for lice eaters is mainly dead cells of the dermis and sebum.
Female insects of both species lay nits in the host's fur, gluing the eggs with a special sticky liquid. It is impossible to see an adult insect with the naked eye. Symptoms of small insects include:
- deterioration of the animal's mood;
- nervousness;
- presence of nits in wool;
- constant scratching;
- wounds on the skin.
Treatment is carried out with specialized drugs for external parasites - Bars, BioVax, Celandine. Neostomazan is considered an effective drug. The emulsion is diluted with warm water and the resulting solution is rubbed on the fluffy’s body. After that, wrap the animal in a towel for 5-7 minutes. After the specified time has passed, the rodent’s fur is dried with a hairdryer.
Helminths
The eggs of parasitic worms enter the rat's body most often through dirty water or raw vegetables and fruits. Severe pathological symptoms with helminthiasis are usually absent. Indirect signs of the disease include:
- deterioration of the pet's mood;
- weight loss;
- change in stool - the appearance of constipation or, conversely, diarrhea.
Helminths are easily removed from the body of rats using specialized drugs. For example, Dirofen, Shustrik, Nemozol. The listed funds are used not only for the treatment, but also for the prevention of helminthiases.
What else do rats get sick with?
The list of diseases of decorative rats can be continued for quite a long time, since these rodents by nature have rather poor health. In addition to the diseases listed above, rats most often suffer from the following pathologies:
- Pododermatitis . In simple words - corns. Appear when kept on rough bedding. Risk factors also include older age and increased body weight. Complications of the disease include suppuration, which is very painful and subsequently breaks through. To avoid such problems, rats' feet are moisturized with baby cream or oil. It is also recommended to replace the bedding with a softer one, such as paper litter.
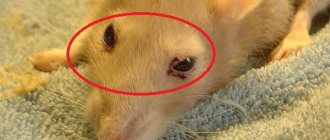
- Conjunctivitis . It develops in improper sanitary conditions - when dust and dirt particles get into the eyes, as well as when the eyelids are damaged (for example, scratching). Symptoms of the disease include: swelling of the mucous membranes and skin of the eyelids, drainage from the eyes leading to souring, decreased visual acuity, and lethargy. Treatment is carried out by instilling special eye drops. The drug and dosage are selected by the veterinarian.
- Periodontitis is a dental disease characterized by gradual loosening and loss of incisors. Poor quality nutrition, predominantly liquid foods, leads to the development of pathology. Symptoms of the disease include yellowing and loosening of teeth, bad breath, and red and swollen gums. Treatment consists of removing damaged teeth.
- Vitamin deficiency . It develops against the background of an unbalanced rodent diet, leading to an acute deficiency of vitamins. Characteristic symptoms: lethargy, dullness and hair loss, drowsiness, mood swings. Treatment is carried out by introducing fresh vegetables, fruits and berries into the diet, as well as adding special vitamin complexes to the feeders.
Every rodent owner should have information about diseases of ornamental rats: symptoms and treatment, causes and prevention - issues that need to be studied before purchasing a pet. Early recognition of the disease and timely visit to the veterinary clinic will not only help to avoid complications, but may also save the animal’s life.
Other diseases
Mouse pox or ectromelia
This pathology affects rats, mice, and less often other rodents. The disease is viral and affects animals that are weakened, for example as a result of severe stress. Rats and mice that are kept in cramped conditions are more likely to get sick.
The main signs of the disease are:
- swelling of the limbs;
- necrosis and ulceration of the epithelium of the skin of the extremities, then foci of gangrene appear;
- the appearance of pustular formations in the tail area (abscesses, boils).
At autopsy, animals are found to have serious pathologies of the liver (cirrhosis, dystrophy) and spleen. There is no treatment for this disease; mortality is 100% of affected animals. Therefore, when diagnosing this disease in pets, it is recommended to euthanize them.
Ear diseases
Otitis media is sometimes reported in rats. It is characterized by torticollis, the discharge of pus from the ear. The owner may feel an unpleasant odor from the animal’s ear even before discharge appears. At the same time, the pet rubs its ears vigorously and regularly.
Eye diseases
Most often this is conjunctivitis. This disease can be caused by debris getting into the pet's eye, injury during a fight, and infection. The pathology is characterized by swelling of the eyelids, redness of the mucous lining of the eye, lacrimation, the appearance of pus and sticking of the eyelids.