What is porphyrin in rats?
Have you noticed any unusual discharge from your pet's nose or eyes? This is a red-brown liquid with a consistency similar to blood. You may think that your pet has suffered an injury, such as a cut. If you want to treat the wound and find out the cause of the discharge, you will see that there is no wound. Such secretions in rats are called porphyrin.
The Veterinary Encyclopedia has a definition of this disease. Porphyrin - in a nutshell - is a red or burgundy-colored substance that resembles blood in appearance and composition. When porphyrin is released, you might think that your pet is crying tears of blood or has bloody snot.
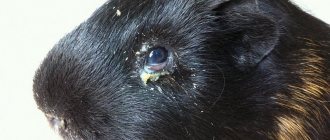
Porphyrin forms on the animal's face near the nose or eyes. These bloody secretions are produced by special glands (Garderian), which are located in the corners of the eyes from the inside.
What does porphyrin look like?
By examining this substance under a microscope, it can be determined that it is similar to blood. It is an organic compound with four pyrol rings. Thus, porphyrin is a group of organic substances that have been identified in the wild. A property of porphyrins is the ability to bind metals.
How to determine if your pet is sick
Porphyrin is very similar to blood. This moment can be determined using a Wood's lamp. In ultraviolet light, this consistency will take on a pinkish color. If such a lamp is not in the house, then you can use hydrogen peroxide. To do this, carefully remove these secretions with a cotton swab. Then peroxide is dripped onto them. Porphyrin will not be able to dissolve and will not change color, unlike bloody discharge. Porphyrin can be a signal of health problems, but not always, so you should pay attention to other symptoms of the disease.
Did you know? In Hinduism, the rat carries the deity of wisdom and prosperity, Ganesha, and is a symbol of successful endeavors and successful attempts.
The main signs that the animal is sick are the following:
- Dark red spots are visible on the nose and eyes. The appearance of such a consistency in excess on one side should also alert you.
- Small wounds on the body, as the rodent often itches.
- Outwardly, the rat looks depressed. Hunches over when sitting, moves with difficulty, spreading his legs. In some cases, it may pull one leg behind itself.
- Movement coordination disorders occur. The rodent may fall on its side, roll in circles, or not pick up food with its front paws.
- Possible manifestation of aggressiveness.
- The animal feels pain when moving.
- The rodent becomes lethargic, indifferent or too active.
- The rat eats poorly, but drinks a lot, feels thirsty, and begins to noticeably lose weight.
- The coat becomes of poor quality - it becomes dull and falls off.
- On the body under the skin you can notice swelling and thickening.
- One eye becomes noticeably larger than the other.
- Breathing becomes heavier. The animal sniffles, sneezes, and makes loud noises. Shortness of breath becomes noticeable.
- Fecal stool changes smell and color without changing the diet.
- Urine also takes on an unpleasant odor and an unusual color. Purulent particles may appear in it. Irregularity in the frequency of urination (too often or, conversely, rarely).
- Discharge with an unpleasant odor appears in the ears. The rodent constantly shakes its head.
- In females, bloody or purulent discharge from the vagina begins to flow.
- In males, any change in color, density, or size of the testicles is noticeable. In a healthy specimen, they should be the same size, cool and without any compaction. The penis should normally be located in the preputial sac.
- It should be noted that a healthy rat’s paws, ears, eyelids, lips, and nose should be pink. When diseases appear, this color may change. So, if it becomes cyanotic, then the animal has problems with blood circulation, heart muscle, anemia, internal bleeding, and so on. A yellowish color indicates a malfunction of the liver and gall bladder.
If the rat was injured during a fight or carelessness, then you need to help it yourself. Wounds should be immediately treated with hydrogen peroxide or potassium permanganate. When the wound is deep and there is bleeding, cold (ice) should be applied. Then, for quick healing, the wounds can be treated with Levomekol. If the claw is damaged and because of this there is blood on the paw, then it must be cut off so that the animal does not feel pain when walking. In addition, if you do not do this, the wound will take longer to heal.
Familiarize yourself with the behavior, care and nutrition of rats at home.
If various damages and wounds are found on the animal’s body, the cage should be cleaned more thoroughly. It is also advisable to cover the rodent’s home with paper for several days (until the wounds heal) and throw in clean pieces of cloth. You should also stop walking for a while.
Is it dangerous?
You can find out whether it is blood or porphyrin yourself. Take some of the substance onto a cotton pad and apply a drop of hydrogen peroxide on it. If the substance begins to hiss and changes color, it means there is blood on the cotton wool.
During a stressful situation or when the rat experiences pain, porphyrin is released in increased quantities. Up to one year, the animal produces a larger amount of this substance than an older rat.
By the age of two, very little fluid is produced by the glands. Often, such discharge is just a natural process, and the intervention of specialists is not required.
But there are times when the help of a veterinarian is necessary:
- liquid is constantly released from the rodent’s nose and eyes in large quantities;
- there is a suspicion that the rodent has mycoplasmosis, diphtheria or salmonellosis;
- if your pet has become slower, does not eat or drink well, or lies down in strange positions.
Treatment methods
If you begin to notice an excess of porphyrin in a rat, then first reconsider its lifestyle and diet. You should stop training and walking outside for a while. You need to carefully examine your pet to see if he has any injuries or signs of illness. Pay attention to whether the animal has lost weight and what its appetite is. It is recommended to take your rat to a veterinarian so that he can accurately determine the cause of the excess porphyrin. It is recommended to immediately isolate the animal from others.
Often the cause of porphyrin discharge from the nose is a cold under the influence of a draft or allergies. An infectious runny nose in this rodent can end badly, and antibiotics usually cannot be avoided (for example, Baytril). It is better if the medications and their dosage are selected by a veterinarian, so if a disease is detected, possible allergens should be immediately excluded, and if this does not help, and wheezing is added to the nasal discharge, then you should urgently consult a doctor.
Important! Rats are not suitable for human food. Vegetable proteins and fatty foods should be excluded from their diet. It's better to give some lean meat sometimes.
If it is not possible to take your pet to the veterinarian, then you should treat it with echinacea infusion and include anti-inflammatory foods for these rodents in the diet:
- bananas, raspberries, plums;
- garlic and onion;
- mustard.
At the same time, unwanted foods should be excluded from the diet:
- raw artichokes;
- chocolate;
- raw legumes, soy products;
- unripe bananas;
- alcoholic and carbonated drinks;
- rhubarb;
- blue cheese;
- spinach;
- raw cabbage;
- raw or sprouted potatoes with sprouts.
Effect of porphyrin
Porphyrin lubricates the nictitating membrane and protects the animal's eyes from bright light. To put it simply, thanks to porphyrin, the animal can blink. Studies have found that in bright light conditions this substance is produced in larger quantities in rats.
The discharge may also increase in response to irritants such as blue light and ultraviolet light.
Also, the volume of secretions increases as the rat grows - the older it is, the more porphyrin. An individual one year old has more such secretions than, for example, a younger animal. And also, on the contrary, with age closer to two years, the production of this substance begins to decline again, and it is already formed in less than a year.
When should you take your rat to the vet?
If your pet rat produces excessive amounts of porphyrin, you may need to visit your veterinarian.
Even with a large amount of porphyrin in the eyes of a rat, the animal can be healthy. However, it is a common symptom of illness or stress and may become more obvious over time. If your rat begins to show other chronic symptoms of illness, stress, or allergies, you will need to take him to the vet.
Some of these symptoms may include large accumulations of porphyrin around the eyes and nose (it will even accumulate on their small wrists and paws), difficulty breathing, wheezing when breathing, loss of appetite, difficulty or absence of urination or bowel movements, excessive sleeping, inactivity, aggression , squealing or squeaking in pain, isolation from cage mates, excessive sneezing, hair loss and more. Your veterinarian can help you identify various causes of stress or illness in your rat.
Prevention
When a rat has no problems and is not sick, its eyes, nose and mucous membranes are absolutely clean. When there is porphyrin in your pet's nose (for no reason), your pet requires the attention of a specialist. At the veterinary clinic, they will take tests and examine the animal, as a result of which it will be possible to understand whether everything is normal or whether there is a disease. In the latter case, the doctor will prescribe treatment at home or prescribe procedures at a veterinary institution.
To prevent the animal from developing bad symptoms, the owner must follow the following rules:
- the cage with the pet should be located in a quiet, calm place - the animal needs comfort;
- The animal should not be stressed, make noise, shout or wake it up abruptly - this will scare it;
- the rat must be fed healthy and wholesome food;
- You constantly need to monitor your pet, its condition, skin and mucous membranes.
If it's not blood, what is it?
Many mammals have third eyelids (the pink bit sometimes seen in the inner corner of the eyes of cats and dogs). Those with a third eyelid also possess an additional lacrimal gland called Harder's gland. In humans, this gland is really small and doesn't really do anything. In rodents (including rats), this gland is larger and has an important function.
This gland secretes a mixture of lipids (oils and fats) and products called melatonin and porphyrin. These secretions lubricate the eye and third eyelid, produce pheromones, and help protect the retina (the back of the eye) from ultraviolet light.
It is these porphyrins, which are secreted by the gland, that are responsible for the red coloration given to rat tears and are responsible for the secretion near the eyes or in the nose.
Treating rats at home
First you need to determine whether your pet is healthy or sick. You can check this yourself, at home. We take cotton wool, collect the discharge from the animal’s face, and then drop a few drops of hydrogen peroxide on it. Let's see if the liquid has changed color. If, under the influence of hydrogen peroxide, the substance begins to hiss and change color, then it is blood, which means that the animal’s skin or mucous membranes have been damaged as a result of injury. If no reaction occurs and the color does not change, then it is porphyrin.
There are also ways to check discharge, for example, using ultraviolet light. You need to put a cotton pad with the substance under an ultraviolet lamp. If the drop starts to glow pink, then it is porphyrin.
How to solve this problem?
An increase or sudden release of red tears is a symptom of a specific problem. If your rat is not healthy, you should take her or him to a veterinarian for a health check.
During the physical exam, your veterinarian will check the front teeth, listen to the heart, lungs, and examine any other problems. Regardless of whether concerns arise during the health check, you should follow these recommendations:
- Reduce stress in the home and try to keep noise levels low.
- Make sure your rat's housing is the right size.
- Provide your pet's cage with toys and various entertainment items that will allow your pet to relieve stress.
- Check the filler material, avoid dusty fillers.
- Do not smoke near pets.
- Make sure there is good quality animal food and enough for everyone to avoid competition.
- Provide fresh water and change it daily.
Causes of increased porphyrin secretion
Increased release of porphyrin is possible for the following reasons:
- bright light;
- decline in the animal's immunity;
- moving to a new home;
- stress;
- pain;
- state of shock;
- sudden change in conditions of detention;
- shortage of drinking water;
- poor quality diet;
- bathing;
- loud noise and vibration;
- animal disease.
Excessive release of porphyrin may indicate infection of the animal with salmonellosis, mycoplasmosis, or diphtheria. In this case, it is necessary to pay attention to the totality of symptoms observed in the animal.
Principles of eye treatment in children
Treatment of ophthalmological diseases in children can be conservative, instrumental and surgical. Conservative treatment is indicated to slow down or stop pathological processes in the eye. It is often possible to stabilize vision and increase its sharpness. Indications for conservative treatment:
- myopia;
- strabismus;
- binocular vision disorders.
For infectious diseases, antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and physiotherapy are prescribed. Parents are strictly prohibited from self-medicating: this can lead to irreversible deterioration of vision and even loss.
Hardware treatment includes computer and psychological vision training. Classes are conducted on special equipment. The set of hardware exercises is selected individually.
Surgical treatment is indicated for cataracts, glaucoma, strabismus, some forms of ptosis and nystagmus. Laser therapy technologies provide the best results.
Eye diseases in children lead to decreased visual acuity, which adversely affects their development. It is important for parents to carefully monitor the condition of the visual organ in their children and when symptoms of diseases appear or before looking at photos of eye diseases
Visit a doctor immediately. Timely treatment of eye pathologies allows you to maintain good vision.
What diseases do rats and mice carry?
Decorative pets can “share” infectious pathologies. The list of potentially dangerous to humans includes:
- plague, typhus;
- "rat bite" (sodoku);
- pneumonia;
- toxoplasmosis, listeriosis;
- tularemia, leptospirosis;
- rickettsiosis, toxocariasis;
- rabies, hemorrhagic fever.
The list of diseases from rats and mice will continue with fungal diseases (ringworm), pasteurellosis, and lymphocytic choriomeningitis. Diseases are transmitted by airborne droplets, through skin lesions and bites. Domestic rodents are less dangerous, but you should still not have close contact with them, kiss them, or eat from the same plate.
Stress
Decorative rats are very people-oriented. Any change in the owner’s life affects the condition of the pet. Changing owners in adulthood is sometimes very stressful for a pet. For this reason, a rat's nose may bleed. Why is this happening? When an animal is in a state of constant nervous tension, immunity decreases, which is why various diseases manifest themselves.
When changing owners, it is important to give your pet time to acclimatize. You should not pick up the animal immediately after moving, but you need to talk to it. The rat needs to be given treats so that it gets used to its new owner. You cannot raise your voice or punish. Rats are smart animals and are easy to train. To establish a good relationship with your pet, you need to spend a lot of time with it. The rat can be taught tricks, you need to communicate with it and play with it. The more attention and care your pet receives, the stronger its immunity and health will be.
What does a sick rodent look like?
A breeder of rats and mice should be aware of a number of signs that may indicate ill health in a pet.
Suspicious symptoms:
- change in behavior (apathy, aggression);
- discharge from the eyes, cloudy cornea, sticky eyelids;
- dull and unkempt fur;
- nasal discharge, mucus, crusts;
- unusual posture, tension.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system are characterized by a lack of air, the rodent falls on its side. Urine will “tell” about kidney diseases; it is cloudy, with impurities, a pungent odor, and discolored. Constant itching, bald spots, and hair loss indicate skin parasites.
All decorative rodents have problems with teeth. In nature, they constantly chew on objects, grinding down their teeth. Pets at home do not have the opportunity to move freely and choose. If the owner does not take care, there is a risk of excessive growth of the incisors, damage to the soft tissues of the skull and bones.
Infectious eye diseases in children
Infectious diseases of the organ of vision are caused by the penetration of pathogenic bacteria and viruses into it. The most common are conjunctivitis, blepharitis, dacryocystitis, keratitis, stye, and purulent eye infections.
General signs of infectious diseases
The visual organs in children are:
- redness of the eyes;
- discharge of purulent contents from them;
- the appearance of dried crusts in the corners of the eyes;
- sensation of a foreign body in the eye;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- discomfort, sensation of stinging and pain;
- photophobia;
- decreased visual acuity.
Blepharitis
With this disease, the edges of the eyelids become inflamed. The causative agents of blepharitis are Staphylococcus aureus and other bacteria, mites, fungi, and worms. Its main features:
- burning of the edge of the eyelid;
- swelling of the eyelid and its redness;
- the appearance of scales on the ciliary edge of the eyelid;
- the appearance of a bright vascular network on the eyelid.
If these symptoms appear, it is necessary to immediately show the child to the doctor. Some forms of blepharitis can cause scars on the eyelids, cornea and even blindness.
Purulent infection
The causative agent of purulent infection is streptococci, staphylococci. Most often this occurs after a foreign body enters the eye. The course of the disease goes through 3 stages: iridocyclitis, endophthalmitis, panophthalmitis.
Iridocyclitis occurs a few days after the injury. Accompanied by severe pain in the organ of vision. The iris becomes yellowish due to the accumulation of pus. With panophthalmitis, inflammation
spreads to the retina, and vision is reduced to the level of light perception. The fundus of the eye has a green or yellow tint.
With panophthalmitis, the pain becomes unbearable, the eyelids swell sharply, and pus flows through the cornea. Even with surgical treatment of this pathology, visual acuity decreases.
Dacryocystitis
This disease can occur in 6–20% of newborns. In this case, inflammation of the lacrimal sac occurs. The disease in newborns occurs due to blockage of the nasolacrimal ducts by epithelial tissues.
Symptoms begin in the second week of a baby's life. This:
- redness, swelling of the inner lower corner of the eye;
- soreness of the inflammatory focus;
- the appearance of pus, tear fluid;
- increase in body temperature.
If the nasolacrimal duct is blocked, the swelling increases and the palpebral fissure narrows. An abscess may develop, and the body temperature rises sharply.
Keratitis
This is an inflammation of the cornea. The disease is caused by bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and less commonly, fungi. With keratitis, burning and pain appear in the eye, lacrimation, and a large amount of pus is released.
Damage to the cornea is accompanied by decreased visual acuity, photophobia, and muscle spasms of the eyelid. If left untreated, an ulcer forms on the cornea and spreads to the internal tissues of the eye.
Conjunctivitis
This is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye. There are bacterial and viral conjunctivitis.
When there is a bacterial infection, a lot of pus is released from the eyes. In this case, the eyelids stick together during sleep. First, one eye is affected, and after a few days the inflammation becomes bilateral.
Signs of viral conjunctivitis are less pronounced. As a rule, the disease occurs against the background of influenza or ARVI. The baby has a lot of clear fluid coming out of his eyes. If it becomes cloudy, this indicates a bacterial infection.
Barley
This is an inflammation of the sebaceous gland and hair follicles. Caused by staphylococci and streptococci. With styes, the eyelid first turns red and then swells. Gradually, the inflammatory process increases with the formation of a purulent cavity. Around the 4th day, the purulent sac breaks through, the pain and swelling subside.
In severe cases, the pathological process spreads to nearby tissues.
How to treat respiratory diseases
Before starting treatment measures, it is important to diagnose the cause of the respiratory disease. This could be a viral infection, poisoning from toxic fumes, allergies, or a cold. For an accurate diagnosis, it is recommended to show the animal to a veterinarian.
If the rat is in satisfactory condition, the animal’s house should be insulated. The cage must be moved to a warm and quiet place. You should not carry the animal in your arms; it needs to be kept at rest. The rat can be given warm milk using a syringe (without a needle). If the animal's condition does not improve, it should be taken to a veterinarian. After diagnosing the cause of the disease, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
It is not recommended to give an animal antibiotics without a prescription, because decorative rats have low immunity, and such drugs can only aggravate an already dangerous situation.
Diseases of rats and mice: a list of obvious ones
Contrary to the myth about their vitality, ornamental animals are not in good health. Typical mistakes in keeping and breeding shorten the already short life of a pet.
What diseases of rats and mice are diagnosed:
- diseases of the ears, eyes;
- infectious pathologies;
- injuries of varying severity and location;
- tumors (benign, malignant);
- disruption of internal organs.
Fact! Rodents do not suffer from rabies, although theoretically it cannot be ruled out that they can become carriers of a dangerous pathology. Such cases are rare.
HIV infection is practically not diagnosed in rodents. There are frequent cases of the formation of malignant neoplasms, and the pituitary gland is the first to be affected.
How often should you wash your rat's eyes?
Inspect your rat's eyes every time you clean them. This procedure should not be performed more than once a week. Most rats can easily tolerate less frequent brushing. These animals are very clean. They will take care of their eye health as part of their daily hygiene routine.
You should clean your rat's eyes every time you see discharge from the eyes. If your rat's eyes keep watering, there's a reason. Cleaning is about eliminating a symptom, not a cure.