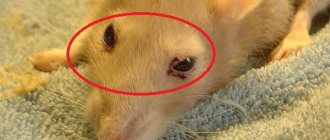
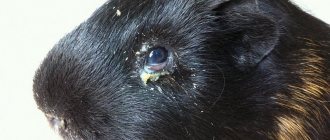
What is it, what are the symptoms
In simple words, an abscess is an inflammation of tissue with the formation of a purulent sac. Pathology develops against the background of damage to the skin with the subsequent addition of pathogenic microflora. At first, the abscess may be quite invisible, especially under thick fur. However, over time, the lump grows and can be observed with the naked eye. The disease in decorative rats is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of a round bump above the skin;
- peeling and redness of the skin in the affected area;
- decreased vitality, apathy;
- increased anxiety;
- refusal to eat.
In some situations - if the animal has a strong immune system, as well as when an abscess forms in the subcutaneous fat, the tumor may simply burst out on its own over time. And then the pet can be put back on its feet at home.
Externally, abscesses in decorative rats are very similar to cancerous tumors. Therefore, it is better not to engage in self-diagnosis, but to have your pet checked at a veterinary clinic. Perhaps the situation is much more serious than it seems at first glance.
But if purulent inflammation has affected deeper tissues and moves inside the body, you cannot do without the help of a veterinarian. The pet will have to be taken to the doctor as soon as possible before complications begin. This includes blood poisoning, which can lead to death.
How does an abscess form?
An abscess is a focal purulent inflammation of tissue. Internal abscesses are localized in various organs and tissues in serious infectious diseases: abscesses of the lungs and liver. External abscesses form on the animal’s body as a result of a violation of the integrity of the skin (scratches, wounds, bites), the penetration of normal microflora into various organs and tissues against the background of inflammatory diseases and decreased immunity.
IMPORTANT!!! The owner himself can infect his pet with staphylococci, which constantly live on human skin.
Subcutaneous abscesses are characterized by:
- the formation of a painful swelling filled with pus;
- thinning of the skin in the center of the abscess, scabs at the site of tissue damage;
- deep damage or general infection of the body may be accompanied by refusal of food, lethargy, and inactivity.
An inflammatory process caused by the proliferation of staphylococci and streptococci develops in the damaged tissue. Around the source of inflammation, lymphocytes form a kind of capsule that prevents the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into healthy tissues. An abscess begins with redness of the rodent's skin, then the affected area thickens, at the end of the process an abscess is formed with soft green or yellow pus inside. Pus is an accumulation of dead lymphocytes, pathogenic microbes and blood cells. The color, consistency and smell of pus can be completely different and depend on the type of pathogenic microflora.
The development of an abscess can go in different ways:
- the purulent contents are destroyed by the body inside the pyogenic capsule, recovery occurs;
- a bulge with pus is formed, which comes out at the site of thinning of the skin, the wound heals and the abscess goes away;
- a convex subcutaneous abscess breaks through, pathogenic microflora penetrates through the bloodstream into healthy organs and tissues, causing inflammation and sepsis;
- the abscess grows deep into the tissue, which is also fraught with septic shock and death.
Causes of abscess
The main reason for the development of an abscess in a decorative rat is the presence of an infectious process. Pathogenic microflora enters the body in the following ways:
- With the development of infectious diseases of internal organs (for example, mycoplasmosis). Moreover, a pet can become infected both from sick cage neighbors and from the owner. There are many known cases of ornamental rats becoming infected with staphylococcus from humans.
- For any damage to the skin - abrasions, scratches, scratches, small wounds. Such damage can result from careless play, fights with other pets, aggressive grooming, or scratching due to allergies.
- When kept in unsanitary conditions. The rat's immunity rapidly deteriorates, and the animal is unable to resist the attack of pathogenic microorganisms.
- After hypothermia or being in a draft. If the animal has a cold, typical signs of ARVI appear along with inflammation.
Only a veterinarian can name the exact cause after carrying out the necessary diagnostic measures. In any case, treatment of the disease must be started as soon as possible, regardless of the nature of its origin.
Etiology of purulent abscesses
An accumulation of pus in a wound does not just form. A clean, dry surface that is slightly hot to the touch will not release any substances. When anaerobic bacteria enter the wound cavity, purulent inflammation begins, which intensifies in the heat and with insufficient hygiene. Causes of abscesses:
- Injuries that an animal can receive while walking, mechanical damage to the skin and mucous membranes;
- Postoperative wounds that were not properly cared for;
- Insect bites, after which the rodent scratches its skin vigorously on its own.
There are two types of abscesses, benign and malignant. With benign inflammation, exudate appears with a large number of leukocytes. During this period, the wound has a good granulation barrier. With a malignant course, a liquid purulent fraction appears, and bumps may form on the body - phlegmons, which are removed surgically. At the same time, the animal’s condition itself worsens: the temperature rises, it feels lethargic, and refuses its favorite treats.
On what parts of the body can it appear?
Purely theoretically, an abscess can develop on any part of the body of a decorative rat. But most often tumors appear in the following places:
- on the paws;
- on the body - on the sides, on the stomach, on the back;
- in the mouth - the situation is complicated by problems with chewing and swallowing food; if the abscess is located next to a tooth, it may have to be pulled out during treatment;
- behind the ears;
- before our eyes;
- on the neck;
- in males in the area of the testes.
Abscesses in the neck area are considered the most dangerous. The fact is that there are many large blood and lymphatic vessels passing through there. Damage to them threatens the animal with sepsis and sudden death. Therefore, under no circumstances should lumps on the neck be opened at home. Such pathologies are treated only in a hospital setting.
Symptoms of paratonsillar abscess
The typical clinical manifestation of PTA is severe sore throat (usually unilateral), fever, and muffled voice. Patients may also complain of drooling and difficulty swallowing.
Trismus (spasm of the masticatory muscles), associated with irritation and reflex spasm of the internal pterygoid muscle, occurs in almost 2/3 of patients and is an important distinguishing feature of PTA in comparison with severe acute tonsillopharyngitis. Patients may also complain of neck swelling and ear pain on the affected side.
How to treat an abscess
To determine treatment tactics, you must contact your veterinarian. In most cases, the doctor will suggest simply opening the abscess surgically. The operation is performed under local anesthesia and takes no more than 15-20 minutes. If deep tissues are affected, the procedure may take 30-40 minutes and will require suturing.
In some situations, for example, when small superficial abscesses occur, it is possible to remove an abscess from a decorative rat at home. The main thing is to wait for the abscess to fully ripen. Maturation will be indicated by softening and darkening of the cone, as well as the appearance of a white head in its central part.
To speed up the maturation of an abscess in a rat, you can periodically apply an iodine mesh to the abscess or tie a piece of cut aloe leaf (cut to the cone) overnight.
To avoid complications, during the procedure you must strictly follow a simple algorithm:
- Wash your hands with soap and, if possible, wear medical gloves.
- Using nail scissors, trim the hair on the affected area. You can do it not at the root, it will cause discomfort to the pet. It is better to leave a small “hedgehog”.
- If there is a crust on the surface of the abscess, you will need to soften it first. To do this, you need to moisten a cotton pad in warm water and apply it to the problem area for 5-10 minutes.
- Apply pressure to the tumor using a smooth movement, moving from the periphery to the center. You can't press too hard. If the abscess is mature, its contents will come out easily.
- As the pus flows out of the wound, you will need to constantly wipe it off with a cotton pad soaked in hydrogen peroxide. The manipulation must be carried out until blood flows from the abscess without any admixture of pus.
- When the procedure is completed, the wound will need to be washed with a solution of Chlorhexidine, Betadine, water and saline. The resulting liquid should be poured into a regular syringe and the wound should be thoroughly washed. After which, gently blot the treated area with a sterile bandage.
At the end of the home “operation” you will need to lubricate the affected area with Oflomelid or Levomekol. To prevent the rat from licking the ointment and smearing surrounding objects, it is better to apply a bandage to the wound and secure it by putting a special postoperative blanket for rodents on the rodent. You can buy the product at a pet store or order it online.
It is worth noting that before opening the abscess, you will need to create a pleasant psychological atmosphere - calm the rat, stroke it, talk to it in a gentle voice, encourage it. If the animal is agitated and clearly nervous, it is better to postpone the procedure for at least a few hours.
Symptoms of the disease: treatment of abscess after tooth extraction and other manipulations
Each defeat gives its own signs, by which it is easy to calculate it if you have the proper experience. Thus, treatment of an abscess after tooth extraction takes place when the patient consults a doctor when he encounters the following symptoms :
- tissue swelling develops at the site of resection or treatment;
- the wound rots, the periodontal mucosa atrophies;
- Acute throbbing pain and bad breath appear.
Body temperature may increase, fever, weakness, and malaise may appear. The general symptoms are the same for all inflammations. It is important to consult a doctor in time , without delaying the moment until complications appear.
Medical offers to make an appointment with a qualified doctor. If the patient’s condition is complicated and going to the clinic is not possible, it is recommended to invite a doctor to your home. The price of such a service is low, but the benefits from it are truly invaluable. The doctor who arrives on call will assess the situation, conduct an examination and prescribe treatment for the abscess in a delicate manner for the patient. In severe cases, urgent hospitalization may be recommended.
Caring for your rat after surgery
Opening the abscess is half the battle. The pet faces a rehabilitation period of 7-10 days ahead. At this stage, the owner must pay maximum attention to his pet. In order for the rat to recover as quickly as possible, the following measures will be required:
- Transplanting a small patient into a separate cage. This is necessary so that healthy relatives do not injure the fluffy during outdoor games. It is better to replace the usual filler with a disposable diaper. It is much easier for a weakened animal to move on such bedding. In addition, it will perfectly absorb exudate.
- Installation of feeders and drinking bowls in free access for the animal. The main thing is that the pet does not have to stretch and be in an uncomfortable position when wanting a snack or drink.
- Thorough cleaning of the cage. The exudate and residual pus released from the wound have a rather unpleasant odor. Therefore, you will need to change the bedding every day and, as necessary, wash the feeders, drinkers and other items located in the cage. This will help avoid re-infection.
- Daily treatment of the wound with an antiseptic. For example, Octenisept, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin.
- Introduction of foods containing probiotics into the daily menu. Apples, yogurt, and kefir will help normalize the intestinal microflora.
- If the apartment is cool, it is recommended to periodically place plastic bottles filled with warm water (but not boiling water) in the cage.
If your pet has received stitches, you may need to take them to the veterinarian to have them removed. However, in most cases, veterinarians suture rats using special absorbable threads.
Diagnostics
In the vast majority of cases, the diagnosis of PTA is made clinically, based on the results of pharyngoscopy (examination of the pharynx). It is confirmed by obtaining purulent discharge during drainage of the abscess or by instrumental studies (most often ultrasound).
Pharyngoscopy reveals a swollen and/or fluctuating tonsil with deviation of the uvula in the direction opposite to the lesion, hyperemia (redness) and swelling of the soft palate. In some cases, there is plaque or liquid discharge in the palatine tonsil. There is an increase and tenderness of the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes.
Bilateral PTA is extremely rare and its diagnosis is more difficult due to the lack of asymmetry in the pharynx, as well as the rarely present spasm of the masticatory muscles.
Laboratory tests are not required to make a diagnosis; they are additionally prescribed to determine the severity of the disease and select a treatment method.
Laboratory tests may include:
- general blood test with leukocyte formula;
- study of electrolytes (potassium, sodium, chlorine) for signs of dehydration;
- strepta test to exclude GABHS;
- culture for aerobic and anaerobic bacteria if the abscess was drained (culture is recommended only for complicated PTA, recurrent PTA, or in patients with immunodeficiency conditions).
Instrumental examination methods - ultrasound, computed tomography, lateral neck x-ray, magnetic resonance imaging or angiography - are not necessary and are performed to exclude other diseases if the diagnosis of PTA is not obvious.
Differential diagnosis
Severe course of acute tonsillopharyngitis . Frequent pathogens are Epstein-Barr virus, herpes simplex virus, Coxsackie virus (herpangina), adenovirus, diphtheria, GABHS, gonorrhea. It manifests itself as bilateral swelling in the throat, hyperemia, and plaque may be present on the tonsils.
Epiglottitis . An inflammatory disease of the epiglottis, usually caused by Haemophilus influenzae. More common in young children who have not been vaccinated against Haemophilus influenzae type b. Progresses faster than PTA. Manifested by sore throat, drooling, difficulty swallowing, respiratory failure.
Retropharyngeal abscess (retropharyngeal abscess) . Purulent inflammation of the lymph nodes and tissue of the retropharyngeal space. Most often observed in children aged 2 to 4 years. During pharyngoscopy, minimal changes are noted. Main complaints: stiff neck, pain on movement, especially when extending the neck (as opposed to the increased pain on flexion seen with meningitis), swelling and tenderness of the neck, chest pain, difficulty swallowing, drooling, muffled voice, spasm of the masticatory muscles ( present in only 20% of cases).
Disease prevention
Abscess in rodents is a rather unpleasant disease that can cause adverse health consequences. Therefore, it is better not to rely on fate and from the first days of the pet’s appearance in the house, start preventing the disease. The following measures will help to avoid the appearance of ulcers:
- Regular examinations of your pet to ensure the integrity of the skin. Even small wounds or scratches require antiseptic treatment.
- Keeping the rat in proper sanitary conditions means regular cleaning of the cage, daily washing of feeders and drinkers, monthly disinfection.
- Protecting your pet from hypothermia. In the winter season, it is better to move the cage with the rat to another room for ventilation. Also, after bathing, you need to thoroughly dry the fur of the fluffy with a towel.
You will also need to remove all objects with sharp corners from the cage so that the pet does not accidentally get hurt. A rat can scratch its paw even on too coarse litter.
An owner who knows what an abscess in rats is and its main symptoms will be able to help his pet in the shortest possible time. The main thing is not to delay your visit to the veterinary clinic and completely trust the specialist.
Aftercare
Opening an abscess for a decorative rat is a serious operation that requires further care for the animal’s rapid recovery.
It is as follows:
- antiseptics can be used no more than once a day;
- isolate the sick rodent from other pets;
- provide him with adequate nutrition and plenty of fluids to restore strength, and also introduce probiotics into the diet to normalize the intestinal microflora after taking antibiotics;
- clean the cage with the rat every day, avoiding any unpleasant odor in it.
Also learn how to identify and treat mycoplasmosis in a rat.