Today, rabbits have become champions for domestic breeding due to their fertility and early maturity. In addition, their meat is very dietary. Therefore, it is very important to know all the intricacies of their cultivation.
Meat, skins, fluff and fertilizer are products that can be obtained by breeding rabbits. This activity is less expensive than, for example, raising pigs or cows.
Over the course of a year, a healthy female reproduces 6 times. This will result in over 25 babies and close to 70kg of meat when they grow up.
Breed selection
Rabbits are bred to obtain skins and fur or meat. For every 10 females, 1 male is purchased, while the smallest farm must have at least 2 males. Based on the purpose of the purchase, the breed is selected.
For meat
Rabbit meat is a dietary product, as it is rich in protein and is easily absorbed by the body.
The best meat breeds:
- ermine;
- gray and white giants;
- white New Zealander.
In just 4 months they will grow and produce up to 3-4 kg of rabbit meat.
For skins
Fur coats, vests, hats and other fur products are made from rabbit skins.
These breeds will pamper their owners with thick, shiny and beautiful skin:
- Viennese blue;
- silver;
- downy white;
- angora.
For meat and fur
Breeds have been developed that are suitable for breeding in both directions.
The owners will be pleased with dietary and soft meat with high-quality skin:
- butterfly;
- Flanders;
- chinchilla.
Where can I buy
It is better to purchase from large breeders or at least from experienced farmers, as this will provide a choice of high-quality and healthy individuals. Honest breeders are concerned about their reputation, so they provide all the information about the individuals they purchase.
What to consider when purchasing
Before purchasing, you need to make sure that the animals are healthy and meet the standards of a particular breed.
Criterias of choice:
- smooth, shiny coat with a sheen;
- there are no tangles or signs of baldness on the fur;
- agile, strong body;
- smooth, without kinks, ears;
- the outside of the ears are covered with light hair, and the inside is pinkish;
- the teeth on the upper jaw are pushed forward more strongly;
- eyes are clean, without redness or discharge;
- look without fear;
- clean skin near the anus, without fecal residues;
- rabbit nose - clean, slightly moist, mobile;
- long, without sagging back;
- soft abdomen without signs of inflammation and tension;
- clean and pink genitals.
Benefit
This business is quite profitable, which is primarily due to the fact that rabbit meat is not yet so common; you won’t find it on the counter next to pork or beef. It is not publicly available; it is often purchased directly from breeders.
Despite the small popularity of rabbit meat, it is considered very healthy and dietary. There will always be buyers for the product because this type of meat is not only perfectly absorbed by the body, but is also an excellent replacement for the usual pork or beef. “Proper nutrition” is very popular now, and not only among those who go on a diet, so rabbit meat is very popular among PP adherents.
In addition to this, a huge number of different recipes are known, which are based on rabbit meat, which cannot be replaced, since the dish will instantly lose its special taste. In some cases, when manufacturers do not want to engage in sales themselves, it is possible to conclude contracts for the supply of goods either to points of sale, or to a cafe or restaurant whose menu includes rabbit dishes. This option may be more profitable than direct sale.
Preparatory activities
Rabbit breeding at home requires some preparation. It is necessary to take the most careful approach to arranging the habitat of fluffy ears. You need to build a rabbitry in advance so that it is completely ready for the arrival of new residents.
Location requirements
Farmers keep eared pets both in the barn and outside in cages. The place for installing the cages is chosen to be level and protected from drafts and winds, with artificial or natural shade. Rabbits do not like high moisture, so during the preparation stage you should take care of comfortable living conditions for the livestock. Provide a wide, convenient approach to the site to ensure easy access to the cages for cleaning and distributing food.
Installation of cages
Comfortable cages are the key to the comfortable well-being of pets, and as a result, an increase in the birth rate and an increase in the number of livestock.
General tips for constructing and installing cages:
- The optimal models will be those houses whose ends and back wall are made of wood more than 1.5 cm thick, and the front wall, part of the floor and the door are made of fine-mesh reinforced mesh.
- It is better to lay the roof from corrugated sheets or ondulin with a small slope so that rainwater and snow do not linger on it. For easy cleaning of the cage, loops can be provided.
- Feeders are made stationary or mobile and are located on the front wall.
- For a small herd, single-tier structures are sufficient, and for a large herd, 2- and 3-tier models are sufficient.
- It is important that there are no holes or cracks in the walls.
- The volume of the house for one rabbit should be no less than 75x60x45 cm.
Queen cell
A separate cage is provided for each pregnant female. The expectant mother lives there awaiting her offspring. Immediately before the babies are born, the cage is supplemented with queen cell.
The queen cell is a closed box with a hole where the female rabbit sets up a nest, and then the newborn babies will grow for the first month of their lives. The box is constructed from wooden slats and lined with plywood sheets. The approximate size of the queen cell is 30x50x30 cm. The hole in diameter should be 15 cm. This imitation of a hole is very cozy and excellent for the birth of offspring.
Cages for mating
At home, special premises for mating rabbits are not built. To produce offspring, the female is simply placed next to the male for 10-15 minutes. Immediately after the end of mating, the female is removed, and if necessary, mating is repeated after 5 days. If the rabbit does not allow the gentleman to approach, she is already considered covered.
Required lighting level
Animals are active while daylight lasts, ideally from 6 am to 9 pm. They need constant access to light, if necessary, window openings or artificial lighting.
Cellular content
Caging is the most popular way to keep rabbits.
Advantages
Raising rabbits in cages has many benefits.
Pros of cellular content:
- it is easy to visually assess the health status of the animals;
- helps to more clearly control reproduction;
- makes cleaning and feeding much easier;
- makes it possible to automate part of the work.
Most importantly, keeping rabbits in cages helps prevent the spread of infectious diseases and the death of the entire livestock if they occur.
Keeping it clean
Cleaning rabbit hutches is not a pleasant task, but there are ways to make the process much easier.
Recommendations:
- Disinfection is extremely important to maintain the health of the livestock. You need to treat the cage by removing the animal and removing any remaining droppings and food. Suitable remedies include burnt lime, a solution of iodine in alcohol, and alkali.
- Queen cells are disinfected after the offspring emerge from them, and also shortly before the female rabbit gives birth.
- You should remove leftover food and change the water daily.
- Feces are removed once every 2 days maximum. This task can be made easier if the floor is lined with mesh and the cage is equipped with a tray.
Features of winter care
Breeding, raising and feeding rabbits during cold weather does not cause any particular problems. Animals can easily withstand cold temperatures because their skin is covered with thick fur. In some cases, the following may be observed: weight loss of individuals, colds and frostbite of the ears.
Recommendations for keeping rabbits in winter:
- Raise the cell level to a height of 90-100 cm above the ground, as frosty air circulates below.
- The temperature in the barn should not fall below 5 °C.
- For warmth and comfort, lay an additional layer of bedding, change it once every 5 days.
- In winter, problems arise with cleaning cages, since in cold weather waste products quickly freeze and are difficult to remove. Provide a mesh floor to allow feces to fall into a removable tray.
- It is better to close the door to the cage with a piece of plywood to prevent drafts from getting inside. However, it is best to install a glass frame on the door instead of a grille, so as not to reduce the light life of your pets.
- Insulate the rabbit house, caulk all the cracks and holes.
Growing in cages
The most affordable breeding option is cages. They have a number of advantages:
- The animal is in plain sight, which makes it possible to monitor its health status and control reproduction;
- It is more convenient to carry out cleaning;
- Facilitates control over the availability and quality of water and feed.
In addition, rabbits are kept isolated or in small groups, which prevents the spread of infections and possible death from them.
- The optimal housing size for keeping an animal alone: L – 72 cm, W – 60 cm, H – 42 cm.
- For a female with cubs: L – 89 cm, W – 78 cm, H – 42 cm.
- The front side of the cage should be mesh, the sides and back wall should be wooden, the roof should be made of corrugated sheets with a slight angle of inclination.
- A feeder and drinking bowl are required inside.
Yamnoye content
The most ancient, but nevertheless good method of raising eared pets is in pits. To raise rabbits at home, the number of which is 20 individuals, you need a basement or cellar 2x2 m and 1 m deep. Three walls are reinforced with wood panels, and the 4th remains free so that the rabbits dig a hole there.
It is better to organize lighting inside, otherwise the animals will breed much worse. You need to clean up as the pit gets dirty.
Advantages and disadvantages
Pit content has both advantages and significant disadvantages.
Pros:
- no expenses are required for the construction of cells;
- saving space;
- the influence of the natural environment on the immunity and health of rabbits: they are born strong and get sick less often.
Minuses:
- the wool in the pits is wiped off, so the method is suitable if you plan to raise rabbits for meat;
- Rabbits that are closely related begin to mate more often, so the breed becomes smaller;
- owners cannot control the mating process;
- It is much more difficult to bring food into such a home.
Approximate business plan
A business plan must be drawn up taking into account prices in the region and the number of individuals. Perhaps the largest part in terms of expenses will be the rent, which can reach 80 thousand rubles. in year. Those who have their own land will only have to pay land tax. Individual entrepreneurs will need to pay taxes monthly.
Next, you need to purchase cells, which will cost approximately 20 thousand rubles. (capacity will be about 20 rabbits). 1 cell will not be enough, i.e. the cost will increase depending on the number of cells. Raising rabbits in pits will be much cheaper. Costs will be limited only to the materials necessary to construct the pit.
Another expense item is the purchase of the animals themselves. The approximate cost of one individual varies from 500 rubles and above (for example, the Giant). This cost is multiplied by the required number of individuals: 500 * 60 = 30 thousand rubles. The cost estimate also includes the cost of feed. As a rule, up to 4 months are allotted for fattening a rabbit, during which time rabbits can eat about 15 kg of feed. Considering that 1 kilogram costs about 12 rubles, the total costs are approximately 30 thousand rubles.
Let's summarize the costs received. According to rough estimates, the required capital for breeding rabbits can reach 170 thousand rubles or more.
Other content methods
There are other technologies for keeping rabbits, among them you can choose the one most suitable for your purposes.
Aviaries
Aviary maintenance will not require large expenses, and the conditions are as close as possible to natural ones. To protect against undermining, you can dig a fence made of poles, slate or mesh around the perimeter to a depth of 60 cm or more. In enclosures, bedding is necessary, but it is changed much less frequently. A third or half of the enclosure should be covered with a canopy, under which there are drinking bowls and feeders.
Sheds and minifarms
Sheds are individual cages that are arranged in a row in tiers. They are equipped with removable pallets or bunker boxes, which are installed separately on 2-3 stands, which makes cleaning easier and faster.
Mini-farms are built from shads, in which up to 1000 heads can be kept. In such farms, rooms with shads are equipped with heating and additional ventilation. This is the most modern, convenient and effective method of keeping and raising eared pets, but it is also the most expensive. Therefore, it is mainly used for large rabbit farms.
General recommendations for arranging a rabbitry
Regardless of which method the farmer chooses, the following recommendations for keeping rabbits must be followed:
- It is advisable to place rabbits at a certain distance from other pets and birds as well.
- If you choose outdoor rabbit breeding, you need to make sure that the area with rodents is surrounded by trees. Of course, this recommendation applies not to small home farms, but to industrial farms. The most suitable tree is birch. If the territory and budget allow, then trees should be planted on the territory of the farm itself. All this is necessary in order to create the necessary climate for animals. The crown of the trees will serve as protection from the scorching sun in the summer, and also protect from the cold in the winter.
Proper feeding
A proper diet allows an animal to quickly gain weight, which is especially important for meat production.
Summer diet
In the summer, concentrates become the basis of rabbit nutrition - 30-40% of the total feed per day. 30% - green food, 20% - succulent, 10% - roughage.
Rules for feeding Eared Ears:
- Give concentrates first, and then greens.
- From the period of weaning until old age, rabbits are fed 3 times a day.
- Pregnant female rabbits and females with babies up to 2.5 months are offered food 4 times a day.
- Daily feed requirements: good concentrate feed – 55 g, grass – 600 g.
- At 6-7 o'clock in the morning, give ½ of the daily norm of concentrate, and 1/3 of the norm of grass. At lunch 15 o'clock another 1/3 of greens. In the evening at 19:00, offer the rabbits the rest of the concentrates, 1/3 of the greens and some roughage.
Winter nutrition
Not only the quality of meat, but also the condition of the animal’s skin depends on the diet in winter.
Winter feeding recommendations:
- If the air temperature outside reaches -15 °C degrees, then you should remove frozen food debris in a timely manner, since animals cannot eat them.
- You can add hay, twigs, silage, heated mash, and pine needles to your diet.
- The average daily doses for one animal are: feed – 80 g, hay – 400 g + additives.
- Watering of the animals is carried out in the morning and evening. For sub-zero temperatures, use warm water or purchase drinking bowls with a heating function.
Vitamins and mineral supplements
Vitamin complexes are used for feeding in late winter, when feed reserves are depleted. Animals need vitamins A and D. To do this, they are added to the diet in the form of concentrate or fish oil.
The amount of fish oil per head depends on the activity and age of the animal:
- baby rabbit – 0.3-0.5 g;
- adult rabbit – 1 g;
- pregnant and lactating rabbits – 3 g.
The lack of vitamin E is compensated by good meadow hay, sprouted grain, and silage. You can add a little bone meal, chalk or bone ash to the food.
It is mandatory to feed your pets salt - 1-1.5 g per day.
Feed for slaughter
Feeding rabbits for breeding requires a balance between carbohydrates and proteins.
Tips for accelerating weight gain:
- Feeding with silage. This is a valuable source of vitamins and minerals, especially in the winter and spring.
- The daily dose of feed is 80 g, and hay is 400 g.
- For intensive growth of young individuals, branch feed is used: willow, willow, and aspen twigs.
- Root vegetables and melons: potatoes, pumpkin or zucchini. They are boiled and mixed with feed granules.
- In veterinary pharmacies you can buy vitamins and minerals and feed young animals according to the instructions to accelerate growth.
Annual feed requirement
At each life stage, rabbits' food needs are different.
Annual requirement (average):
- Breeding rabbit or rabbit in the period between matings: feed - 4.46 kg, silage - 3.2 kg, hay - 1.2 kg, greens - 4.5 kg.
- During the mating period: concentrates - 4.2 kg, hay - 1.5 kg, silage - 3.8 kg, greens - 5.6 kg.
- For a pregnant rabbit: concentrate – 16.8, meadow hay – 6 kg, root vegetables – 15.6 kg, green grass – 23 kg.
- Nursing mother: feed - 62.4 kg, silage -57 kg, green grass - 83.4 kg, hay - 21.1 kg.
- For a young rabbit: concentrated granules - 10.1 kg, silage - 40 kg, greens - 12 kg, hay - 3.1 kg.
What not to feed
Young animals under 3 months should not be given complementary foods in the form of grass and succulent feed. The first time, give new types of food a little at a time and monitor the condition of the livestock and the type of feces.
Rabbits should not be fed:
- wet herbs (given dried or dried);
- milkweed, datura, celandine, tansy, wormwood, aloe, arisema, beans, cornflowers;
- seeds and mushrooms;
- any bakery products;
- sugar;
- figs;
- milk;
- avocado;
- nuts and peanuts;
- corn and pea husks.
Depreciation expenses
In order to breed these animals, it is necessary to invest financial resources. The total cost must include the following costs:
- It is necessary to purchase cages or equip another type of housing for animals.
- You must have the necessary vaccinations.
- You will need to provide a supply of food for the rabbits.
- Rent of premises or land may be required.
- Equipment for slaughtering and dressing hides.
- Purchase of breeding animals and their transportation.
The profitability of a business depends on the costs incurred and the income received. It must be taken into account that mating occurs 5-6 times during the year. Usually 6-8 individuals are born. After 3-5 months, the rabbit’s weight reaches 3 kg.
Reproduction
At first glance, breeding rabbits at home may seem difficult for beginners, but in cage conditions, tracking the process is quite simple.
Nutrition during mating
Animals should eat a balanced diet, not lose weight or gain fat, otherwise breeding rabbits will be problematic. Add a pinch of salt and 2 g of fish oil and chalk. Give food three times a day.
Conducting mating
Puberty of rabbits occurs at 3.5 months, but mating should be carried out no earlier than the 5th month.
How to properly breed rabbits:
- The female must be in heat. Signs: loss of appetite, pinching down, genitals swell and turn bright pink. The male is active, young and of average fatness.
- The maximum number of coats per day for a male is 2 times.
- Remove all accessories from the cage. Place the female in the cage with the male. The ideal temperature for the process is 24-25 degrees.
- The end of the covering is when the male falls on his side and purrs. Immediately remove the female and do not allow repeated coverings of the same rabbit.
- After 5 days, place the animals together again. If the female avoids intimacy and does not allow the male to approach, it means that the first mating was successful.
Definition of pregnancy
The entire period of gestation of a female rabbit requires special attention from the breeder to her condition.
Signs of pregnancy:
- Refusal of mating.
- On the 15th day, in the back of the rabbit’s abdomen, you can feel a couple of chains of small bulges, 2-3 cm in size.
- A week before giving birth, the female makes a straw nest.
- During the day, she plucks her down and puts it in the nest.
- During the entire pregnancy, the rabbit eats heavily and quickly gains weight.
Pregnancy and childbirth
The gestation period for cubs is 28-35 days, on average about 1 month. The time depends on the size, health and breed of rabbits. The more embryos a rabbit has in her belly, the sooner they will be born.
It is better to isolate a pregnant female from stress: noise, din, bright light source. During childbirth, there should always be a lot of water in the cage, since the new mother can eat her babies from thirst.
During pregnancy and after giving birth, treat your rabbit to carrots, cabbage and beets, herb hay, and vitamins.
Features of winter breeding
In winter, mating is not very active; instead, pets gain weight in order to warm themselves by increasing body weight. The actual coating procedure is planned on a day when severe frosts are not expected.
Pregnant females do not suffer in winter if you carefully take care of the arrangement of their home: insulate it, provide artificial lighting in the queen cell.
Biological characteristics of rabbits
The rabbit is a rodent mammal belonging to the Zaitsev family. The domestic rabbit is descended from the wild South European one.
By mating a domestic and wild rabbit, you can get good offspring. Crossing a rabbit with a hare is impossible because they have different biological characteristics.
Cubs can manage without the help of a female rabbit at 3-4 weeks of life. They begin to eat food on their own without stopping drinking milk.
The time that the rabbits will spend in the queen cell depends on the amount of milk from the mother. Milk production can be determined by the appearance of the cubs. If their skin is smooth, without folds, and they lie quietly, then the milk content is high. The highest occurs after 4 births.
Obesity and low physical activity of the animal can reduce milk production.
An obese female cannot become pregnant. To avoid this problem, you need to reconsider her diet: increase the amount of greens, limit the consumption of grain and mixed feed. And give more space so she can move.
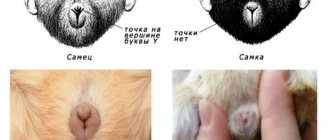
Rabbits see much worse than they smell. If you give someone else's baby to a rabbit, she will identify it by smell, regardless of color. She will not accept strangers. Rabbits also get used to new food by sniffing for a long time.
The rabbit gnaws exclusively plant food, which is why it has a unique teeth structure. He has molars and incisors that grow throughout his life. The animal has no fangs. The incisors on the front are covered with a ball of enamel, and are sharpened in the process of eating food.
The digestive system of rabbits is well developed. The stomach is voluminous and is characterized by high digestibility of food due to the high acidity of gastric secretions.
The food can remain in the animal’s stomach for 3-10 hours. The rabbit's intestines are 10 times longer than the length of the animal (up to 6 meters).
Another peculiarity of rabbits is that they eat their excrement at night. They contain a large amount of protein and vitamin B. This is how rabbits have adapted to replenish the required microelements by the body.
Slaughter
The slaughter process is the most unpleasant action, but if you keep rabbits for meat, you need to study the intricacies of the process. Experienced rabbit breeders advise starting slaughter no earlier than the animal is 4 months old and never slaughter pregnant or lactating rabbits.
Procedure:
- Before the scheduled day, place the animal separately and do not feed it so that the stomach and intestines are cleansed.
- Remove the rabbit carefully, holding it by the hind legs.
- Using a stick wrapped in rags, deliver a precise blow to the back of the head.
- Place the carcass on spacers, pierce the artery through the mouth, remove the eyes and wait until the blood drains completely.
Diseases
The body of rabbits is quite delicate and does not have a strong immune system. For this reason, they often pick up various infections. Transmitted from rabbit to rabbit, diseases very quickly affect the entire flock. Typical symptoms of an infectious disease in a pet include:
- lack of appetite;
- body temperature is more than 39 °C;
- discharge from their eyes and nose;
- stomach upset;
- patchy dull fur.
Infectious infections in rabbits cannot be treated. When the first symptoms are detected, the sick animal must be removed from everyone. But this measure does not always protect the flock from death. The best way to prevent infection is timely vaccination.
Taking care of your health
Diseases of eared pets can lead to the death of an entire herd, so you should respond in time to any changes in the appearance and behavior of pets.
Basic diseases and prevention
All diseases are divided into contagious and non-contagious.
Main diseases of rabbits:
- Pneumomycosis is a fungus of the respiratory tract. Manifested by sneezing, heavy breathing and yellowness of the mucous membranes. It is necessary to monitor the cleanliness of cages and feeders and change food on time. The disease cannot be treated, sick individuals are killed, and the cage after the animal is filled with formaldehyde to kill microorganisms.
- Scabies is caused by a mite. The skin peels around the ears, nose, eyes, spreading to the whole body. Only disinfection and lubricating the affected areas of the skin with turpentine will help.
- Ear scabies - sores and blisters on the skin. The treatment is the same, but the cage is disinfected with creolin.
- Bronchitis. Occurs from drafts and sudden temperature changes. It is treated with Tromexin, Brovaseptol and Brovafom, and the cage is additionally insulated.
- Worms are accompanied by weight loss. For prevention purposes, you should systematically clean your pets' houses, change drinking bowls and feeders, treating them with steam. “Naftamon” helps sick animals.
- Conjunctivitis B - appears due to mechanical damage to the eyes and a lack of vitamin A. Visually, it is redness and swelling of the eyes, constant production of tears and the appearance of eye pus. Animals' eyes should be washed with 2% boric acid.
- Mastitis. The rabbit's udder becomes hard and red. Wounds and ulcers appear on it. The house must be kept clean and be sure to call a veterinarian for an inspection.
- Myxomatosis is the most dangerous disease. Tumors appear in the form of nodules on the head, near the anus and genitals; drooping pet ears also signal a disease. It is necessary to administer the vaccine to animals in a timely manner, to disinfect rabbit household items and the premises where they are kept.
The purchased rabbit must be kept in quarantine for 3 weeks before being placed with other animals.
Vaccination
In order for rabbits to get sick less often in the future, timely vaccination should be carried out.
Approximate vaccination schedule:
- at 45 days – from hemorrhagic disease;
- at 2 months – from myxomatosis;
- 3 months after the previous one – from myxomatosis;
- repeated against hemorrhagic disease - 2 weeks after the third.
Castration
Veterinarians advise castration of rabbits between the ages of 4 and 25 months. It is not recommended to castrate individuals over 4 years old, and it is prohibited for those over 6 years old.
Pros of castration:
- increased life expectancy, improved health;
- reducing the risk of genital diseases;
- stopping “marking” of territory;
- reduction of conflict between males;
- acceleration of weight gain;
- improving the condition of the skin.
Minuses:
- pain and need for rehabilitation;
- likelihood of complications;
- high costs.
Diseases and their treatment
Rabbits often get sick. When raising rabbits, it is necessary to observe preventive measures to prevent diseases:
- disinfection of cells and equipment;
- vaccination against viral diseases (vaccinations against myxomatosis and rabbit distemper are mandatory).
Diseases of rabbits are divided into:
- infectious-viral;
- bacterial and invasive;
- non-infectious, caused by physical factors - fractures, bites, poisoning.
Myxomatosis
A dangerous disease of rabbits that is subject to mandatory control. Infection occurs through:
- contact of healthy animals with sick ones;
- infected equipment;
- after being bitten by mosquitoes carrying the disease.
The first symptoms of the disease appear 2-5 days after infection. Symptoms include:
- conjunctivitis;
- watery eyes;
- swelling of the ears, head, limbs, lower abdomen, external genitalia.
Sick rabbits are not treated; healthy ones are vaccinated prophylactically; cages and premises are protected from mosquitoes from July to October.
Rabbit Plague
A viral disease characterized by an extremely acute course. Within 48 hours, in some cases 18 hours after infection, the death of all rabbits in the herd occurs. 2-3 hours before death, severe weakness, shortness of breath are observed, a serous runny nose appears, and the rabbits make sudden movements. Sick rabbits are not treated.
Prevention - vaccination of rabbits at the time of weaning from females, repeated vaccination is done after 6 months if they remain for further reproduction.
Pasteurellosis
Bacterial diseases include pasteurellosis, caused by Pasterella multocida bacteria, which live in the respiratory tract of every healthy rabbit, causing no harm under favorable conditions. The disease begins with a runny nose and eyes, and the mucus becomes purulent as the disease progresses.
Rabbits cough, sneeze, have difficulty breathing, and die from suffocation. The disease can have an acute or chronic course. Treatment includes the use of antibiotics, sulfonamides, and serums.
Coccidiosis
The parasitic disease caused by protozoa of the genus Eimeria can take an intestinal or hepatic form. Infection occurs through the gastrointestinal tract; young rabbits are more likely to get sick, immediately after weaning. Sick animals are drowsy, apathetic, do not eat, and diarrhea appears, leading to dehydration and death. Treatment includes administration of medications recommended by veterinarians.
Raising rabbits can be a good activity for rural residents, providing healthy, tasty meat and a satisfying business. Raising rabbits in the backyard is an additional source of income, it is not difficult if you provide them with the proper conditions and protect them from mistakes.
Mistakes of inexperienced farmers
Beginning farmers can make mistakes when starting to raise rabbits.
The most important of them:
- the female is not taken away from her partner on time after mating;
- young males who are not capable of fertilization are used for mating;
- lack of control of the nest after birth;
- feed not suitable for rabbits;
- untimely slaughter;
- non-serious attitude towards vaccination;
- wrong choice of breed.
Raising rabbits can be a profitable family business. With proper care, the initial costs will pay off within a year, and the home business will generate good income.
How should newborn rabbits be cared for?
After birth, about 7 new little rabbits are born. They look very tiny, as evidenced by their weight: about 60 g. It can also be said that at first newborn babies are completely defenseless, as they are born completely blind and without fur. In order for the rabbit to have enough milk, she needs to have constant access to water. If this is not done, there is a high probability that the young will be eaten by their own mother.
During breastfeeding, you need to minimally interfere with the natural process, because a rabbit that has the smell of a person on it can most likely be rejected by the rabbit, after which it will inevitably die. After the rabbits reach the age of 1 month, they need to be taken away from their mother and placed in separate cages. At this age, the stocking density can be about 12-18 birds per cage.