Cute fluffy hamsters are very active and inquisitive animals. During periods of activity, funny Syrian and Djungarian hamsters can scurry around in their cage for hours, run along stairs and tunnels, and play in the hands of their owners. Sometimes you can notice that the hamster's hind legs have failed. This disease can occur in pets at any age, even with the best care.
Explicit and implicit symptoms
Obvious symptoms are characterized by a rapid course.
They appear along with pain and weakness in the limbs. It becomes difficult for the animal to make habitual movements, and soon the legs lose sensitivity. Loss of response to a stimulus is the most alarming sign, called paresis. When their legs fail, old dogs fall and turn their heads to the side. Because of fear, they completely lose coordination and their breathing quickens. The sequential occurrence of the listed symptoms lasts no more than a day. The condition worsens not only with physical activity, but also during sleep. Sudden movements in this situation are provoking factors, not the real reasons.
It is almost impossible to recognize the disorder at the initial stage, since the initial symptoms are difficult to diagnose. Possible subtle
symptoms include:
- loss of activity and rapid fatigue;
- lack of strength to move after a long sleep with subsequent restoration of mobility during the day;
- unsteady gait with limping or dragging legs;
- the occurrence of clicking in the joints while walking;
- refusal to go up or down stairs;
- wobbling of the butt under intense loads.
A sick dog shows anxiety and is reluctant to respond to the owner’s call. Due to the intermittent pain that occurs only with sudden movements, he tries to remain motionless for as long as possible.
This is interesting: A 5-year-old German Shepherd is losing hair, has blisters on her paws, and has plaque in her ears.
Hereditary diseases of Djungarian hamsters
The most common diseases of Djungarian hamsters are type 1 diabetes and tumors. Most often these are hereditary genetic diseases.
Symptoms of diabetes in dzhungarik:
- the dzhungarik began to drink more than usual - hamsters of this breed in a healthy state drink very little;
- the dzhungarik pees a lot (if you missed the moment of increased thirst, then you will notice an unusually large puddle in the toilet corner;
- the hamster’s urine has changed its smell, it has become pungent and unpleasant;
- atypical activity or, on the contrary, lethargy of the hamster;
- The pet eats a lot and at the same time loses weight sharply.
To do this, buy special test strips. They are sold in every pharmacy. The test should be done after the hamster has slept for the longest time of the day. Place it in a clean container, and after the hamster urinates, collect the urine in a syringe and drop it onto the marked square. By the color change, after checking the instructions, you will find out the amount of sugar in the animal’s urine. If it exceeds the norm, most likely the hamster has diabetes.
Types and causes of occurrence
There are two forms of the disease: idiopathic (primary) and secondary. In the first case, the problem occurs for no apparent reason and is often hereditary. This is the type that occurs in young people.
The secondary form of restless legs syndrome occurs against the background of various diseases and conditions. The list of reasons includes:
- injuries to the brain or spinal cord (bruises, concussions, compression, etc.);
- vitamin deficiency, lack of minerals: most often the development of the disease is provoked by a deficiency of vitamins B1, B9, B12, as well as calcium and magnesium;
- pregnancy, especially its second half (the problem is associated with the increased need for microelements);
- renal failure and electrolyte imbalance that occurs as a result of it;
- diabetes;
- anemia (lack of iron in the blood);
- chronic or one-time severe stress;
- excessive physical activity;
- multiple sclerosis;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- disruption of the thyroid gland, accompanied by an excess or deficiency of its hormones;
- alcohol or drug abuse;
- diseases of the veins of the lower extremities: varicose veins, phlebitis, thrombophlebitis;
- amyloidosis: severe systemic disorder of protein metabolism;
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
- Parkinson's disease;
- excessive caffeine consumption.
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: celiac disease, dysbacteriosis, Crohn's disease;
- use of certain medications (antidepressants, antihistamines, etc.).
The development of pathology in childhood often occurs against the background of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Steps
Part 1
Assess the situation
- Examine the injured hamster.
The hamster's body is very small, and its bones are small and fragile, so these furry little ones often suffer various injuries. Fortunately, not in all cases you will need the help of a veterinarian. Quickly examine the injured animal and assess whether its injuries appear to be minor (such as minor cuts and scrapes) or severe (such as broken limbs or severe bleeding).
Call your veterinarian or veterinary clinic.
If your hamster is seriously injured, call your veterinarian or veterinary clinic immediately and let them know that you will soon be visiting them with an animal that will require urgent care. Keep in mind that not every pet doctor is trained in treating small pets (such as hamsters, mice, and guinea pigs). If your veterinary clinic doesn't have specialists who care for hamsters, ask if they can recommend a clinic or veterinarian who specializes in this group of pets.
- During your phone call, ask your veterinarian what first aid you can provide to your pet before you bring it to the clinic.
- Gather the necessary materials to assist.
If you determine that the injury does not pose a serious threat to the hamster's life, you can treat the animal on your own. To get started, gather all the materials you need for treatment, including clean towels, cotton swabs, several 10 ml syringes (without needles) and sterile gauze pads measuring 5x5 cm. In addition, you will need a bottle of sterile saline solution, wound cleaning solution ( You can buy Betadine, but a regular iodine solution) and antibiotic ointment will do.
Part 2
Treatment of small wounds on a hamster
- Give the hamster the opportunity to recover on its own.
- When you treat the wound yourself, it gives you the opportunity to prevent an abscess from forming. While cleaning the wound, you can control how well you cleaned it (which is difficult if your pet licks the wounds on his own).
Hamsters are very resilient animals, so small wounds in these animals heal quite quickly without any treatment. If your pet has minor cuts or scrapes, it is wise to leave the animal alone and allow it to fend for itself. In such cases, hamsters lick and clean their wounds, thereby promoting rapid healing.
Limit your hamster's mobility.
This will give you the opportunity to treat your pet's wounds. Before treating wounds, wrap your hamster in a small, clean towel to limit the animal's movement. An injured hamster becomes very restless, so you need to protect yourself from possible bites.
Treat the wound.
Take a syringe and fill it with some sterile saline solution. Carefully pour the solution onto the edges of the wound and blot the liquid using one or two gauze pads. Repeat the procedure several times to clean the wound and remove necrotic tissue.
Take a second syringe, fill it with a little iodine solution, pour it onto the surface of the wound, and then blot the solution with several gauze pads. Using a cotton swab, apply a thin layer of antibiotic ointment to the wound surface.
- An antiseptic helps destroy microorganisms that cause inflammation.
The iodine solution leaves stains on the skin that are difficult to wash off, so you may want to wear medical gloves before treating the wound.
Whatever injury your pet has suffered, it is important that he has the opportunity to rest and recover in the safe, quiet space of his crate. Place bowls of water and food near where your hamster usually sleeps. Find a warm, quiet place in the house for the cage where the hamster will not be disturbed.
Determine the cause of the injury.
Of course, you don't want your pet to get hurt again, so try to determine where exactly your pet got hurt this time. Look for any toys in the cage that have sharp edges that could cut the animal's skin. Carefully inspect the rods: perhaps there is a sharp end of the wire sticking out somewhere, on which your pet was scratched.
Part 3
First aid for serious injuries
- Provide first aid to the animal.
- Take care of the injured animal when you return home from the clinic.
Once your veterinarian has given your hamster the care it needs, there are a few things you'll need to do to give your hamster a calm environment to recover at home. In addition to painkillers, the doctor usually prescribes a cold compress, which should be applied to the injury site to reduce inflammation. Hamsters are very small animals, so an incorrectly applied cold compress can not only cool the injured area, but also cause general hypothermia in your pet.
- Wrap your hamster in a warm cloth while you apply the compress, and continue to warm your pet after the procedure is completed.
If your pet has an infected wound, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics, which you will need to give to your pet.
If your pet has been seriously injured,
you need
to take him to the vet as soon as possible. Providing first aid to your pet correctly will help stabilize its condition and increase the animal's chances of staying alive until it reaches the veterinarian's hands. First aid is extremely important if your hamster is bleeding.
Take the animal to the veterinary clinic.
The doctor will provide qualified assistance to your pet. When you take your hamster to the vet, wrap the animal in a towel and place it in its regular carrier. This will help provide a calm, safe environment for the animal during the trip.
Hamsters are one of the tiniest pets; they require special attention and timely care. With insufficient care, these pets are quite often susceptible to diseases, so the main task of the owner is to recognize the disease by symptoms, and begin treatment for their pet as early as possible and in a timely manner. Paws are the most vulnerable parts of the body of domestic rodents. They are quite often exposed not only to bruises and dislocations, but also to fractures. Animals most often injure their limbs during stress (the appearance of a cat or dog), during peak sexual activity, or during play. What to do if your hamster breaks his leg and how to help him cope with the injury?
The most common factors of injury among hamsters are:
- incorrect for a particular rodent species. When purchasing a hamster, take care of its complete safety. Choose reliable and safe cages. Sometimes the height of the cages can reach 70 centimeters, and it’s scary to imagine what a fall from such a huge height onto a plastic object, such as a feeder or house, would be like for a baby. And just the fact that the hamster broke its leg is not the worst thing. Sometimes the outcome for you may be more disastrous.
- entertainment and auxiliary accessories for the physical development of the pet. Buying “sports” and additional accessories - a lattice running wheel, all kinds of ladders and dividers between floors, into which your pets’ legs often fall. Try to purchase items that will ensure your pet's safety as much as possible.
We wrote in detail about how to set up a cage for your pet in.
By eliminating these causes, you can eliminate the possibility of some injuries. We all know that it is easier to prevent injury than to subsequently treat a furry rodent in pain.
Paresis and paralysis (plegia) in dogs
Depending on the depth of the disorders and the degree of loss of limb function, paresis and paralysis, or plegia, are distinguished.
Paresis
- This is a weakening of voluntary movements. Plegia (paralysis) is a complete inability to make voluntary movements.
Paresis can be:
- partial (outpatient) - voluntary movements are impaired, but the dog is capable of moving;
- complete (non-ambulatory) - control over voluntary movements is completely lost; with paraparesis, the animal can only move by dragging its hind end.
Such an assessment may be somewhat subjective, but it helps to most fully describe the clinical picture in each specific case.
Depending on the level of damage to the spinal cord and the involved limbs, there are:
- paraparesis (pelvic limbs involved);
- tetraparesis (all four limbs are involved);
- monoparesis (only one limb is affected);
- hemiparesis (extremities on one side of the body are affected).
Similarly, para-, tetra-, and monoplegia are distinguished.
Symptoms
A paw fracture is an injury to the bones of the fore or hind limb. Depending on the injury received, the following types of fracture are distinguished:
- Open. Characterized by damage to the skin and protrusion of the bone.
- Closed. With such a fracture, the integrity of the skin is not damaged, but the bone is partially or completely broken.
- Strong pain. When you feel the sore paw, the animal may behave aggressively, try to get out of your hands or bite. In this way he reacts to the pain in a broken limb.
- Bend the paw. In order not to touch the sore paw, the rodent bends it under itself.
- Unnatural mobility. A tarsus fracture may be characterized by a dangling limb.
- With an open fracture, the bone is visible.
- Swelling or hematoma may form near the site of injury.
- The hamster may refuse to eat.
A bending does not always mean that the hamster has broken its leg. Perhaps it's just a dislocation. The condition is painful, but less dangerous than a fracture. How to distinguish a dislocation from a fracture? When a limb is dislocated, the animal may partially rely on the injured paw and limp. The same symptoms accompany a bruised paw.
Causes of onychomycosis
Onychomycosis can be caused by various types of fungi. First of all, these are dermatophytes. In second place are yeast fungi of the genus Candida, which are always present in small quantities on human skin (they most often affect fingernails). Infection with mold fungi is also possible (they usually accompany other pathogens. Isolated infection with mold fungi is typical not for our climate, but for the tropical climate).
The risk of fungal infection increases with age. In children, nail fungus is very rare, and, conversely, in older people it is detected relatively often. Moreover, men suffer from onychomycosis more often than women.
The age specificity of the fungus is explained by the fact that our local immunity decreases over the years, while the natural defense of a young body, as a rule, well suppresses the activity of fungi, preventing them from colonizing the nail plate. There is a dependence not only on local immunity, but also on general immunity. A weakened general immune system is a favorable background for the development of any fungal infection.
For fungi of the genus Candida, it is enough that there are problems with the immune system: they simply begin to actively reproduce. Fungi of other species still need to somehow get into our body from the external environment. Some types of fungi can be carried by animals. Molds are found everywhere; they are able to reproduce without a host. However, in most cases, the fungal infection spreads from person to person.
Mushrooms love a moist environment. Therefore, fungal infection often occurs in places where humidity is high. These are swimming pools, saunas, locker rooms, gyms. Wearing socks and shoes on wet feet can also be a trigger.
If there are wounds and cracks, they allow the infection to penetrate directly into the tissues, avoiding the need to storm the protective barrier that forms the surface of our skin.
The spread of fungi is facilitated by negligence in personal hygiene: you should not use someone else’s slippers, soap, or towel. It is precisely because not every family follows this rule that nail fungus often becomes a family disease.
Damage to the nail usually begins at the edge. Dermatophytes penetrate under the free edge of the nail plate (into the subungual recess). In this case, the pathological process develops mainly in the nail bed. The second route of penetration of fungi is from the nail fold. Candida fungus usually affects the posterior nail fold first (paronychia occurs), and only then does the nail itself suffer. One type of dermatophyte (T. mentagrophytes) can penetrate directly through the nail plate.
Hair loss and other diseases of hamsters
Dandruff, scratching and baldness in hamsters can be caused by ectoparasites, pathogenic dermatophyte fungi, endocrine system disease, and sometimes tumors. The severity and duration of skin diseases in hamsters depends on the cause.
Many of these diseases, such as dermatophytosis or lichen in hamsters, are contagious and can be transmitted to humans. Therefore, if you notice suspicious symptoms, immediately take your hamster to a veterinarian.
Hamsters are often troubled by Demodex mites, which can be transmitted from one hamster to another. Only a veterinarian can identify the cause and prescribe the correct treatment.
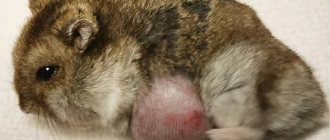
Abscesses are an accumulation of pus in a limited cavity. Pus accumulates under the skin, sometimes forming large, painful swellings on the surface of the hamster's body. Abscesses can form due to cuts and scrapes in the skin. If sharp food particles injure the wall of the cheek pouch, a cheek pouch abscess may develop, and the cheek will appear full all the time. Abscesses require treatment by a veterinarian.
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis is a disease of viral etiology; it can be asymptomatic in hamsters, but there is a danger of infection in humans. When buying a hamster for a child, remember the possible risks; conduct a preventive examination of the animal by a veterinarian.
How can you tell if your paw is broken?
Even animals that do not leave their cage often suffer bruises, sprains and dislocations. Often these types of injuries go unnoticed because the animal in pain reduces physical activity and hides in its house until the discomfort passes. The fracture can be open or closed:
Closed fracture
- the limb hangs unnaturally;
- the animal moves on three limbs, pressing the injured paw to the body;
- the injured paw is swollen and there is noticeable bleeding;
- the hamster tries to move as little as possible and refuses food.
If possible, it is recommended to take an X-ray to make a final diagnosis. A closed fracture is often confused with a dislocation. A modern digital device is capable of detecting fractures in even the smallest animals.
Open fracture
With an open fracture, the picture is clearer; it is impossible not to notice it. Added to the above signs is the most obvious one:
the skin is damaged and a piece of bone is sticking out.
Therapeutic measures
If your hamster is limping, you can cure it yourself, but it is better to consult a veterinarian. Treatment of fractures: if closed, apply plaster, give painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs; in open cases - surgical intervention, in severe cases, amputation. If you do not contact a specialist in time, the bones may heal incorrectly, and lameness will remain for life. An untreated open fracture can turn into gangrene, which can lead to death. First aid instructions:
- Give your pet peace.
- Determine the extent of damage if you have sufficient knowledge.
- Lubricate the swollen area with Levomikol.
- Treat with an antibacterial drug and bandage the paw for an open fracture.
Treatment of wounds and cuts: Hamsters usually lick them themselves, but if an abscess has formed, then go to the vet immediately. He will open it up and process it with education. You will carry out further treatment yourself. You will need to regularly give the animal antibiotics and treat the wound. Treatment: moisten the edges of the cut with saline solution, then blot with gauze. Do this as many times as possible until the wound is clean. After cleaning, apply iodine solution and blot the area. Finally, cover the wound with antibacterial ointment.
Measures to prevent limb paralysis in rabbits
You can save your pet not only during illness, but also before it
Preventing the disease is very important, because proper care of the animal will significantly reduce the risk of disease
Rabbits are creatures just like humans and need variety in their diet. There is no need to focus on one microelement, because its excess will lead to the same consequences as a deficiency. Good things should be in moderation!
Stressful situations are unacceptable
It is important to provide pets with a quiet existence so that they live a long life: do not disturb the rabbits with bright light, do not hurt them or spank them, do not allow them to meet other pets, and when transporting, narrow the animal’s field of vision with a small box. Periodically allow them to walk in relative freedom.
If a rabbit is kept in a cage all the time, its limbs will simply atrophy.
It is necessary to ensure cleanliness in the enclosure, otherwise the long-eared animal will easily pick up some kind of infection or parasite.
In conclusion, I would like to add that one of the most important rules is to be attentive to your pet and monitor its health! It is easier to prevent a problem than to treat its consequences.
Hamster's wet tail
“Wet tail” or proliferative ileitis is an infectious disease of hamsters. It is characterized by a severe course, a high degree of contagiousness between rodents and the possibility of death of the animal. The main symptoms are wet fur on the back of the hamster's body around the tail, severe diarrhea with an unpleasant odor, and decreased or absent appetite. If a disease is suspected, it is necessary to immediately isolate the sick hamster from the rest, disinfect the cage, and it is better to get rid of its contents. This disease does not tolerate delaying a visit to the veterinarian for professional assistance. Dehydration is a serious threat to a hamster's life. Prevention of “wet tail” comes down to maintaining hygiene, living conditions and a balanced diet for hamsters.
Diarrhea can be caused not only by the causative agent of proliferative ileitis. Errors in feeding, other infections or the use of antibiotics lead to similar symptoms: bloating, diarrhea, decreased appetite and lethargy. For an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to examine the hamster at a veterinary clinic.
Physiological edema
Swelling of the legs can be caused by physiological reasons, that is, be a consequence of special circumstances affecting a healthy body, and not a manifestation of a disease. These reasons include:
- salty food. Salt binds water. And if you eat a lot of salty foods, especially at night, you may notice swelling in the morning;
- alcohol. Alcohol also retains water. Therefore, after drinking alcohol, a person looks puffy. The problems are not limited to the face; the legs can also swell;
- hot weather. In the heat, blood vessels dilate as the body tries to normalize heat exchange. More blood flow means the risk of congestion and swelling in the legs increases;
- prolonged sitting or standing. If the legs are in one position for a long time, the blood stagnates in them, which leads to swelling. The worst thing is to sit with your legs crossed. Standing in one place for a long time is also not useful. Swelling of the legs is typical for people in standing professions - hairdressers, salesmen, cooks;
- uncomfortable shoes. If shoes disrupt normal blood circulation in the foot (high heels, narrow arches, tight straps), wearing them will lead to swelling.
When to sound the alarm?
Few owners notice changes in the condition of their pets in the early stages of the disease. But early diagnosis is the key to a speedy recovery of the animal. How can you tell if your pet has health problems? Of course, conduct an external examination and observe the fluffy for a couple of days. You should:
- assess the animal’s activity: if Homa suddenly becomes lethargic, he is clearly unwell;
- watch your appetite. Healthy animals love to snack. If a pet refuses even its favorite treat, it is seriously ill;
- check the weight. An adult must weigh at least 90 g; for all other breeds, including Djungarian hamsters, the weight must not be less than 30 g;
- examine your pet's face. The eyes should be shiny, without cloudiness or mucus. Nose – cool, without discharge. Check your ears for flaking. Pay attention to the incisors: they should grow evenly;
- make sure that there are no skin growths or tumors on the neck, armpits and abdomen;
- inspect the butt and the area of fur under the tail, they should not be wet or dirty;
- the living space also needs to be examined: if the rodent has an intestinal disorder, the stool will be liquid, and if it has cystitis or diabetes, you will understand it by the smell.
If at least one sign is detected, it is worth taking the fluffy to the veterinarian so that he can make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
2.Causes of leg pain
There are several categories of problems that can cause leg pain, discomfort and the other symptoms listed above. Let's try to figure it out in more detail.
Firstly, it may be problems with the skin of the legs
. Symptoms and the diseases that cause them may be:
- If while walking you feel as if you are walking on stones or pebbles, it may be plantar warts on the lower part of your foot;
- Areas of dense and hard skin on the heels may appear due to calluses, blisters on the skin or engorgement of the skin due to uncomfortable shoes, walking barefoot;
- Redness, peeling of the skin, burning and itching between the toes or on the bottom of the leg are signs of foot fungus (mycosis). Another possible cause is dermatitis due to the shoes you wear;
- Red, swollen, and tender skin around the nail may be symptoms of an ingrown toenail or nail infection (paronychia);
- Redness, swelling of the feet, pain in the feet when walking or touching are signs of a possible bacterial infection. You can become infected in public showers, swimming pools and other similar institutions.
The toe joints are a very vulnerable area.
. And it is with the joints of the toes that there are more problems than with any other joints in the body.
- Big toe joint pain, redness, swelling and tenderness that suddenly appears in the big toe joint can be caused by gout. The same symptoms can appear due to infection;
- If you have a swelling or lump at the base of your big toe, it may be a bunion;
- A lump on the outside of the little finger may be due to bunion;
- Toe joint pain, stiffness, and swelling are common symptoms of bunions, arthritis, lupus, or gout.
Foot pain may appear in the front of the foot or in the heel.
- Sharp pain in the bottom of the heel can be caused by plantar fasciitis;
- Pain in the back of the heel or ankle are symptoms of Achilles tendinitis, or as it is also called, Achilles tendinitis;
- Pain that worsens before or after exercise but improves during exercise may be caused by a broken bone in the leg (usually a metatarsal);
- Small bone spurs under the heel bone that cause heel pain may be a heel spur;
- Pain in the midfoot occurs due to flat feet;
- Pain in the back of the heel or a lump in this area is a symptom of a type of bunion.
Many diseases can affect the nerves of the foot
, causing foot pain, numbness, tingling and burning.
- Foot pain, burning, tingling, or numbness between the toes, especially between the third and fourth toes, and the same sensation in the forefoot may occur due to swelling or thickening of the nerve in the forefoot;
- Pain, numbness, or tingling that starts in the back or buttocks and moves down the leg may be caused by sciatica due to a pinched nerve;
- Weakness and pain in the ankle, which is often accompanied by numbness, can begin due to a pinched nerve in the ankle (tarsal tunnel syndrome) or sciatica;
- Burning in the legs, numbness and loss of sensation appear due to poor blood circulation. This problem is more common among people with diabetes or peripheral artery disease.
As you can see, the causes of leg pain, pain in the feet, ankles, toes, and other causes of discomfort in the legs can be very different. Therefore, if you experience symptoms such as pain in the legs, swelling of the legs, cramps in the legs, burning sensation, numbness, tingling in the legs and toes, paleness or blueness of the legs, you need to consult a good doctor. A specialist will help determine the cause of discomfort in the legs and tell you how to deal with them.
Reasons caused by temperature violations
To understand whether your hamster is sick and what to do if it does not move, carefully examine the furry animal. If the pet breathes calmly and evenly with his eyes closed, and this state was not preceded by symptoms of the disease, it is obvious that this is hibernation, similar to the one that hamsters fall into in the natural environment.
Staying in a “coma” allows them to save their lives during the cold period (with a lack of food and insufficient lighting). If the cause of this condition is overheating of the animal’s body, then this is much more dangerous than hypothermia. A furry pet's body does not have protective mechanisms to withstand heat or sunstroke. Overheating, in most cases, provokes death.
Did you know? The name "hamster" comes from the old German word "hamstern", which translates to "treasure".
Heatstroke
The natural habitat of the Djungarian hamster is the steppe, and the Syrian hamster is semi-desert, but the body of these rodents is defenseless against overheating as a result of extreme heat - the body is covered with thick fur, does not secrete sweat, and the animal does not have a function that allows it to breathe through the mouth. Rodents cannot tolerate high air temperatures, and exposure to direct sunlight is harmful to them. At increased risk are obese, elderly, pregnant and confined individuals.
Symptoms that indicate overheating include:
- immobility - the animal lies on its side;
- heavy breathing with an open mouth;
- trembling body;
- red eyes and mouth;
- increased body temperature;
- weakened and “indifferent” state;
- the rodent twitches, which indicates the presence of convulsions.
Preexisting unfavorable conditions may contribute to the condition of heat stroke:
- transportation of the ward in a car;
- placing the cage with the pet on a windowsill or balcony, where the baby is not protected from direct sunlight, or near heating appliances;
- the room where the rodent lives has not been ventilated for a long time and has a high level of humidity.
The maximum permissible temperature at which a furry pet cannot exist permanently, but only for 2-3 days, is +28°C.
Important! Due to heat stroke, the animal dies in most cases. To save him, it is advisable to take measures immediately.
If your pet overheats, begin providing first aid yourself.
- Cool the animal's body without a sudden drop in temperature. To do this, you can place the animal on a damp towel, tile, or on the surface of a ceramic dish, moisten the ears and paws with cool water. Do not use ice cubes to wipe the fur. It is forbidden to immerse a rodent in cold water. Such a temperature change can trigger a heart attack, which can lead to death.
- The cause of overheating may be dehydration of the pet's body. To replenish the lack of vital fluid in an immobile rodent, sterile Ringer's solution or sodium chloride is injected under the skin. The dosage of the medicine varies depending on the type of animal. So, the Syrian and representatives of other large breeds are injected with 4–8 ml; the Djungarian, which is small in size, will need 2 ml. The baby will become vigorous and cheerful after a few days, during which problems with coordination are still usually observed.
- It is not recommended to start anti-shock therapy before the arrival of a ratologist. If the condition of your ward becomes more and more critical, then you can use Prednisolone with a concentration of 30 mg/ml, as well as an insulin syringe and give an injection into the muscle of the hind leg: for a Syrian hamster - 0.1 ml, for a Djungarian hamster - 0.05 ml. If the animal experiences convulsions, then it is given one drop of No-shpa; if it loses consciousness, it is given the same amount of Dexamethasone. For large Syrian rodents, double the dose. Then the therapy is continued, drinking Traumeel S 1-2 drops twice a day. Ensure the temperature in the room is within +24...+26°C, feed your pet three times a day for 3 days with a cocktail of Gamavit, saline solution and five percent glucose - two drops of each substance.
The temperature at which proteins coagulate in the blood and organs of a hamster is +44°C.
It is critical, so the pet is almost impossible to save. If the patient’s body temperature persists for quite a long time, then there is no hope for a favorable outcome. Death can be instantaneous or after a few days, during which all body functions gradually fade away. Important! To check the degree of dehydration, pull the animal's fur upward. If she continues to stand and does not return to her previous position, then this indicates an unsatisfactory condition of the body.
If the rodent managed to survive, then in the first day after heat or sunstroke, residual effects of overheating may be observed: the animal lies on its side and barely moves. Neurological disorders are caused by swelling of brain tissue. If the outcome is favorable, problems with coordination will gradually disappear.
Coma or hibernation
The cause of the hamster's state of torpor may be a low temperature background in the room where the animal is located. For example, as a result of turning off the heating or as a result of leaving a window open for a long time in winter. A lack of food for 2-3 days can also provoke a “coma” or hibernation. During this state, the animal's body will be cool to the touch, but soft. This means he is alive. To determine the heart rate, use your thumb and forefinger to grasp the hamster's chest under the paws.
The heart beat in a coma is slow—about one beat every fifteen seconds. The breathing intensity of a sleeping hamster with its eyes closed is quite difficult to determine due to its small size - it is calm and even. In the wild, with the arrival of cold weather, individuals of the Hamster family begin to hibernate. Thus, they manage to survive the winter season with short daylight hours and no opportunity to get food.
Important! Avoid being in a coma
-
to do this, ensure the temperature in the room with the rodent’s home is above +20°C, as well as the penetration of a sufficient amount of sunlight into its cage, not forgetting to regularly fill the feeder and drinker.
To awaken the patient, the cage is placed in a room where the air temperature is not lower than +20°C. After 2-3 days the rodent wakes up. By the time you wake up, fill the feeder and water bowl. After hibernation, the rodent has little energy, so it rushes to make up for its lack by eating intensively. If your pet does not receive enough food after hibernation, this can lead to serious liver problems. Such a long awakening of a rodent is similar to how it wakes up in natural conditions of existence.
You can “raise” a pet from hibernation faster:
- Wrap your pet in warm wool or downy fabric, place it in its home and move it to a room with high air temperatures.
- You can fill 3-5 plastic bottles with hot water. Place them in a row and place a cage on top. The heat will keep the hamster warm in his home.
If, after waking up from a “coma,” the animal walks poorly, sneezes, coughs, and has a wet tail due to diarrhea, be sure to consult a veterinarian. The best option would be for a doctor to visit your home to examine the rodent, because the baby is not yet ready for transportation after hibernation.
Symptoms and treatment of pathology in a child
Clinical signs of myopathy in children:
- change in gait;
- weakness that does not go away with rest;
- delayed motor development;
- flaccid, flabby muscles;
- atrophy (thinning) of muscles;
- curvature of the spine is a manifestation indicating weakness of the muscular corset.
Negative processes manifest themselves in children in early and teenage years, but since myopathy develops slowly, it can go undetected for a long time. In addition, children are able to compensate for muscle deficiency by using other, healthy muscles more actively.
The most common changes are observed in the areas of the shoulders, legs, arms, pelvis, and chest. With this disease they are always bilateral and symmetrical.
As the disease progresses, movement disorders appear:
- it is difficult for a child to sit up from a lying position;
- movements are abnormal, “wrong”;
- when walking and/or running, fatigue quickly sets in;
- the child has difficulty maintaining balance and often falls;
- It is difficult for a child to climb stairs.
Disturbances in appearance may also appear:
- protruding ribs;
- very thin, as if overtightened, waist;
- flattened chest;
- slouch;
- Irregular shape of legs - thick calves and thin thighs.
Hamster diseases - main symptoms
Any disease in rodents certainly affects their appearance and behavior. A healthy hamster is active, curious, has a good appetite, has well-groomed fur, calm breathing and clear eyes.
Common symptoms include:
- decreased activity
- food refusal
- weight loss
- sniffling, sneezing
- discharge from the eyes and nose
- diarrhea, wet fur around the tail
- hair loss and scratching on the skin
If you notice one of these symptoms of hamster disease, then you need a veterinarian. Visit your doctor as soon as possible.
It is not uncommon for hamsters to develop respiratory infections, which can lead to severe pneumonia (pneumonia). At first, the owner may notice that the hamster is hiding in the house, sneezing, and there is discharge from the eyes and nose. If left untreated, breathing becomes heavier and the hamster may breathe with its mouth open and make wheezing sounds. Pneumonia can lead to death. Early contact with a veterinarian can save your hamster's life.
Can a rabbit live with paralysis?
It is difficult to answer this question unequivocally - it all depends on the cause of paralysis and the ability of the animal’s body to resist the disease. Some rabbits die in a matter of days or even hours, while others successfully fight the disease and eventually recover. But even if your rabbit's paws do not return to normal, there is a chance that he will be able to live his previous life, provided that you take upon yourself to ensure his comfortable existence. You will need to independently carry it from place to place, bathe your pet often, supplement its daily diet with vitamin supplements, and prevent the appearance of bedsores.
Now, knowing a little more about such a disease as paralysis of the limbs in rabbits, you can prevent the development of this disease in your pet. And also, if necessary, provide him with first aid and, together with the doctor, determine the correct course of treatment for the animal.
Treatment
It is impossible to figure out if a hamster has a broken leg or a dislocation at home. The most correct action in this situation would be to contact a veterinary clinic, if possible, to a veterinarian. This is a veterinarian who specializes in the treatment of rodent diseases. With the help of visual examination and palpation of the damaged limb, the specialist will make the correct diagnosis. In some controversial cases, radiography may be prescribed. Treatment depends on the severity of the injury. In case of a closed fracture, a plaster cast is applied, and the animal is given painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. If open, surgical intervention is possible, in some cases amputation. If the fracture is not treated, the leg will heal itself over time, but not correctly, and the hamster will remain lame for the rest of its life. If an open fracture is left untreated, gangrene may develop. Then death is inevitable.
It happens that it is not possible to seek help from a specialist. This may be due to the fact that there is no veterinary clinic in the locality. What should an owner do when his hamster breaks its leg?
- Ensure complete rest;
- Try it yourself, knowing the symptoms, determine the severity of the injury;
- Apply Levomikol ointment to the site of swelling;
- In case of an open fracture, be sure to treat the sharpening bone with an antibacterial agent. Cover the paw with a bandage.
In two to three days you will see the effectiveness of your actions. If the limb begins to dry out or turn black, then amputation is necessary. In some cases, rodents amputate the diseased limb on their own, gnawing it off.
Why does a hamster fall on its back?
If your pet maintains mobility, appetite and cheerfulness, then there is no need to worry. However, if the hamster falls down as if paralyzed, pulls its hind legs, becomes lethargic and apathetic, then you should immediately contact a veterinary clinic.
There are physiological and pathological reasons for this behavior. To determine them, you need to carefully monitor the accompanying symptoms and the general condition of the hamster.
Pet needs a sand bath
In the wild, hamsters use sand baths to combat parasites. The rodents fall on their backs, somersault, quickly jump up, and then repeat everything again.
Pets do the same on an instinctive level. Therefore, if the hamster begins to tumble backwards, then it is worth offering him a bath of fine, purified sand.
Defensive stance
The reason a hamster falls on its back may be a defensive reaction. No matter how strange it may seem, the defensive stance of a rodent is characterized by:
- falling on your back;
- freezing in this position for several seconds;
- pressing ears tightly;
- raising all four paws up.
This pose shows that the animal is belligerent. Therefore, you should not disturb him - at this moment he may bite or scratch severely.
Falling from height
A hamster's hind legs may fail due to injury from a fall from a height onto its back. In this case, severe bruises, dislocations, fractures of bones and the spinal column may occur, hematomas may form, compressing muscles and nerve endings.
If the hamster's hind legs fail, you should try to limit the pet's mobility and inform the veterinarian about damage to the leg or spine. Subsequently, it is necessary to remove all ladders and crossbars from the cage, replace the bedding with soft paper napkins, and additionally introduce foods rich in calcium into the diet.
The pet is sick
A condition in which a hamster's hind legs suddenly fail may indicate a stroke or heart attack. These pathologies can be triggered by severe stress, which is caused by:
- loud sounds;
- sudden switching on of very bright light;
- the appearance of unfamiliar animals in the room;
- moving to a new place of residence;
- lack of attention from the owner or, conversely, his excessive intrusiveness.
Paralysis of the limbs, in which the hamster's hind legs give out and it falls on its back, can be the result of age-related changes. In most cases, this symptom indicates the approach of death.
Diseases that can cause hind leg failure in hamsters include:
- malignant tumors;
- inflammatory processes in internal organs;
- hernias;
- infections affecting nerve tissue.
In this case, the following symptoms also indicate the development of hamster pathologies:
- apathy;
- lack of interest in food;
- disheveled and unkempt fur;
- dirty genitals and tail.
If your hamster has any of the listed signs, you should immediately show your pet to a veterinarian. After all, pathological processes in rodents develop rapidly, and any delay can cost the animal its life.
Sometimes hamster owners note that the animal begins to step on some paw with caution. They immediately begin to panic, but it is better to calm down and analyze why the hamster is limping.
- Causes of lameness
- Types of injuries and symptoms
- Fractures
- Bruise or dislocation
- Wounds and cuts
- Therapeutic measures
- What to do after visiting a veterinary clinic?
What to do after visiting a veterinary clinic?
Once you get your pet home, keep him calm and continue to follow your doctor's instructions. Apply a cold compress to your hamster, but be careful so that the animal does not become hypothermic. Disturb your pet less, do not pick him up. This can lead to complications or new injuries. Thus, if a hamster is limping on one leg, it is most likely a traumatic injury. Prevention consists of avoiding the listed causes and regular examination of the animal.
When purchasing a hamster for home, the breeder must understand that he takes responsibility for the well-being and health of the animal. The hamster is unpretentious in keeping, compared to other pets, however, it requires attention and care, because there is a whole list of diseases to which it is susceptible. In addition to colds and diseases of internal organs, various types of injuries are diagnosed in rodents. Often - mechanical damage to the limbs. This includes fractures and dislocations. They are easy to recognize. In both cases, the hamster's injured paw swells. The animal bends it under itself and reacts painfully to palpation. So, you understand that the hamster broke its leg. What to do in this case?
Rehabilitation after a fracture
Complete recovery of a paw after a fracture can take 2 to 4 weeks. During this period, mobility restrictions are still relevant. If for some reason the animal needs to be returned to the cage, all ladders, running wheels and other toys should be removed from it. Change the litter regularly.
After consulting a doctor and providing first aid, the pet should be closely monitored. After the first three days, you can judge the success of the therapy. If the paw begins to dry out or turn black, you need to urgently consult a doctor - amputation is required. However, sometimes animals simply gnaw off an injured limb; this instinct is inherent in them by nature.
Eye diseases in hamsters
Conjunctivitis is a fairly common eye disease in hamsters. The development of the disease in hamsters can be provoked by particles of sawdust or hay that get on the mucous membrane of the animal’s eyes, or by failure to comply with hygienic conditions of detention. Characteristic signs of conjunctivitis are discharge from the eyes, sticking of the eyelids. The animal experiences severe discomfort and scratching its eyes with its paws only aggravates the situation.
Treatment involves rinsing the eyes with saline solution or lotion and using specialized drops prescribed by your doctor.
Alcoholism
Regular alcohol abuse that lasts for years also causes polyneuropathy. The disease in an advanced state is fraught with partial or complete paralysis of the lower extremities and other unpleasant manifestations:
- Fatigue;
- Cramps of the calf muscles;
- Weakness that does not allow standing on your feet.
Initially, older patients suffering from alcoholism complain of tingling and pain in the legs, gradually developing into numbness. Such patients have many reasons not to seek the help of doctors. This greatly complicates the situation, especially when drinking alcohol continues.
In this case, it is especially difficult for the patient’s relatives. Not only are they trying to fight the underlying disease of a loved one – alcoholism. They also have additional concerns - caring for the patient, servicing him, and an increased amount of housework.
How to diagnose the disease?
The appearance of weakness in the legs is a reason to consult a general practitioner.
He will conduct a clinical examination, study the medical history and, if necessary, refer you for consultation to specialized specialists, for example, a geneticist or a neurologist. Since weakness in the legs can be caused by a number of diseases, a comprehensive examination is necessary to understand what exactly caused the clinical picture. This may include:
- Neurological examination;
- Laboratory diagnostics - general and biochemical tests of blood, urine, etc.;
- Genetic examination - if the development of hereditary muscular dystrophies is suspected;
- Instrumental diagnostics - ultrasound, radiography, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, electroencephalography, electromyography, etc.
Caring for a pet with paralysis
During the rehabilitation period, avoid traditional medicine. Natural components often cause allergic reactions and are ineffective outside of complex therapy.
Review your diet, making it easily digestible and fortified. The main emphasis is on calcium and B vitamins. Eliminate any foods that cause fermentation - legumes, baked goods, unprocessed cabbage, spinach, apples, mushrooms and dried fruits. Due to flatulence, pain worsens, so it is more difficult for the pet to survive the healing of wounds left after surgery, if any.
Wash your pet regularly to prevent bedsores and unpleasant odors. At first it will be difficult for him to get to the toilet, so lay out disposable diapers and regularly change his sleeping place. With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable, and the lost movement function gradually returns.
The meaning of a mole on the foot in men
A large nevus in a man is considered a sign of fidelity to his wife. Such a person is a reliable friend and business partner. Moles on both legs promise a happy marriage.
The guy with the pigment formations on his soles is pretty smart. He often falls in love and has many friends. He is also distinguished by other character traits:
- rich inner world;
- resourcefulness;
- caring;
- seriousness;
- romance.
Such men reach great heights and have a strong character. They will never leave a loved one in trouble and rarely need money. A mole on the right heel speaks of the insight of its owner.
Nevi have different meanings depending on their location on the foot:
- between the second and thumb – excessive fatigue, poor vision;
- between the third and second fingers - susceptibility to influenza, poor immunity;
- between the fourth and third fingers - the risk of developing varicose veins, hemorrhoids, and nasopharyngeal diseases;
- between the fifth and fourth fingers - a weak nervous system.
Birthmarks that influence fate usually have the following shapes: triangle, square, circle, cross or star.
Vintage basket
Here we are dealing with a representative design in the style of modern rural fashion. Best suited for lovers of cycling or short distance travel on scooters. The basket itself is woven from flexible willow and equipped with an openwork wire lid, which prevents the cat from wanting to get out while moving. At the first glance at such a carrier, one is reminded of idyllic pictures from centuries ago, when food from the market was transported in a similar way on bicycles. The entire structure is conveniently attached to the steering wheel using leather straps and does not require much time for preparation.
The advantage of the option under consideration is, of course, its original design and originality. The downside is limited functionality. Although, if desired, the basket can be used for its intended purpose.
Price – 1,128 – 1,708 rubles.